StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Physics
- Investigating the Hookes law by Determining the Spring Constant
Free
Investigating the Hookes law by Determining the Spring Constant - Lab Report Example
Summary
This research "Investigating the Hooke’s law by Determining the Spring Constant" shows us an interesting experiment proving Hooke's law. The spring constant of a mass was determined both statically, by measuring its stretch when subjected to loading, and dynamically…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER97.6% of users find it useful
- Subject: Physics
- Type: Lab Report
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: demetris57
Extract of sample "Investigating the Hookes law by Determining the Spring Constant"
Investigating the Hooke’s law by determining the spring constant By of the of the School (University)
City
Date
Abstract:
The main aim of this experiment was to investigate the Hooke’s law by determining the spring constant for a spring. This was done plotting a graph of extension and force proportional to each other. The spring constant of a mass was determined both statically, by measuring its stretch when subjected to loading, and dynamically, by measuring the period of a mass hung from one end and set into vertical oscillation. The resulting value was 53.55 7.46 N/m, indicating that the springs behavior follows the Hookes law to within the limits of accuracy of the experiment.
Introduction:
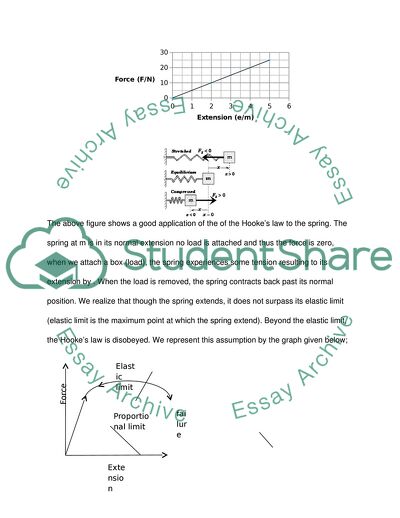
The Hook’s law states that the displacement of spring is directly proportional to the force experienced by this spring. If by any chance the force surpasses the limit of flexibility, the spring shape is changed permanently. In symbols, we can express this as follows;
In this case, is the spring constant which measure the firmness of the spring with unit newton per second (N/m). The above expression implies that an increase in the value of k results to the spring becoming stiffer. on the other hand represents the extension of string after force applied.
The above figure shows a good application of the of the Hooke’s law to the spring. The spring at m is in its normal extension no load is attached and thus the force is zero, when we attach a box (load), the spring experiences some tension resulting to its extension by . When the load is removed, the spring contracts back past its normal position. We realize that though the spring extends, it does not surpass its elastic limit (elastic limit is the maximum point at which the spring extend). Beyond the elastic limit, the Hooke’s law is disobeyed. We represent this assumption by the graph given below;
There exists a relation between stress and strain and this relationship is called young modules and it represents the elasticity of the object.
Thus young modulus is given as;
Hypothesis
The change in length of spring (extension) is directly proportional to the force applied, that is, greater force applied will result to a greater extension (change in length) of the spring. This hypothesis is supported by the formula of force, , where is the applied force, is the spring constant of the spring, and is the change in length or extension of the spring. Since the spring used is the same, the spring constant will always be the same for any value of force applied and extension of the spring.
Theory
The relationship between a load force and a light spring was the first determined by an English scientist, Robert Hooke (1635-1703) in the 17th century. Hooke’s law states that when an elastic material is subjected to a force, its extension is proportional to the applied force. The value of is constant for a particular spring. When an elastic material is subjected to a force, its extension is proportional to the applied force, the value of is constant for a particular spring.
Method:
We set up the apparatus as shown below, but with no load.
We set the pointer to be exactly on zero, this made it easy for the extension to be measured as each 100 g mass was added. Next we carefully added 100 g masses and recorded the extension each time. This was repeated until 900 g was reached.
Results
Mass/g
Force/N
Extension/cm
Extension/m
0
0
0
0
100
0.98
30
0.3
200
1.96
59
0.59
300
2.94
91
0.91
400
3.92
122
1.22
500
4.9
149
1.49
600
5.88
180
1.8
700
6.86
219
2.19
800
7.84
249
2.49
900
8.82
280
2.8
Calculations
Discussion
In overall, the experiment was conducted with minimum errors and the given procedures were followed to the latter. There were 9 data points. The experiment was aimed at investigating the relationship the force (F/N) and the extension (e/m).
We plotted a graph of force (F/N) against the extension (e/m), so as to determine the gradient (which is the spring constant). The x-axis represents the extension (in metres) while the represents the force (in newton).
According to the Hooke’s law, the graph remains linear until it exceeds the elastic limit. We consider the graph to be accurate but not precise. Hooke’s law states that the spring extension and the applied force are directly proportional to each other so the graph should pass through the origin, which is shown in the graph. The spring constant was found to be 53.55 N/m which is less than the expected accurate result. The more accurate result should approximately be 55 5 N/m. This clearly shows that there were some flaws/errors in this experiment.
Most error is a result of measuring judgments, parallax (eye sight) and non-zero reading. Some error has been found because a ruler where not on surface. Many other experimental errors may be found either systematic or random errors. The length measured by the ruler is said to be more than the measured number, this number was considered because it is the minimum measurement we were using. In the gradient we used 7.46 as the highest error possibly to occur and it’s higher than expected value which must be ±5. Using well developed equipment and fixing the ruler with the clamp stand may help reduce the errors.
Conclusion
From the workings, it is clear that there is a positive linear relationship between force (F/N) and the extension (e/m). The gradient of the graph represented the spring constant and this result was found to be . Though the graph is accurate we cannot certainly be 100% precise since it is subject to human errors.
References
Breithaupt, j. (2011). Physics. 3rd edn. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Bueche, F. J., (1980). Introduction to Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Third Edition,
McGraw-Hill, N.Y.
Wilchinsky, Z., (1939). "Theoretical Treatment of Hookes Law," Am. J. Phys. 7, 134.
Walker, J. (2011) Principle of Physics. 9th edn. California: John Wiley & sons inc.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Investigating the Hookes law by Determining the Spring Constant
Loaded Spring Oscillator, Hooke's Law
The restoring force F, is found by multiplying the spring constant K, to the displacement from equilibrium x; F=-Kx.... Therefore the springs can be combined to cater for specific spring constant.... For springs in series, the equivalent constant is equal to the following: 1/Keq = 1/K1 + 1/K2 Therefore the equivalent spring constant is the reciprocal of the answer from above.... If the springs are in parallel the equivalent spring constant is equal to the sum of the spring constants of the springs used....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Assignment
Preparation of Aspirin: Hookes Law of Elasticity
Moreover, from the resulting calculated spring constant, it can be concluded that different springs have different spring constants hence this dictates the amount of load the spring can support.... "Preparation of Aspirin: Hooke's Law of Elasticity" paper states that springs have different spring constants hence this dictates the amount of load the spring can support.... It can be concluded that the springs obey Hooke's law and the elasticity characteristics of the spring were determined....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Essay
Hookes Law: Springs and Oscillators
"Hooke's Law: Springs and Oscillators" paper investigates, preliminarily, the relationship between force and stretch as a stepping stone in the determination of the relationship between frequency and mass in an effort to determine the dynamic spring constant.... Lab Report Hooke's Law Springs and Oscillators This experiment investigates, preliminarily, the relationship between force and stretch as a stepping stone in the determination of the relationship between frequency and mass in an effort to determine the dynamic spring constant....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Lab Report
Hookes Law Laboratory
= -kxThe constant k is called the spring constant.... We will determine the spring constant, k, (K which is the stiffness of the spring), for an individual spring using both Hooke's Law and the properties of an oscillating spring system.... From Equation 1, we see that we need to multiply this quantity by g to calculate a value for the spring constant of k = 217.... 6 N/m, is the spring constant, which agrees with the value found by taking the average of the calculated spring constant....
3 Pages
(750 words)
Lab Report
US Legislature and United Kingdom Legislature Comparison
Legislative Studies, spring, vol.... Powers of Parliamentary Second Chambers', The Journal of Legislative Studies, spring,
... The more effective committee systems respectively provide arenas for determining differences and environments, which foster compromise and decision.... This function appears after a law is agreed on and includes monitoring executive performances for efficiency, probity and fidelity....
17 Pages
(4250 words)
Research Paper
Homicide, Forensic Science and Criminal Justice System
orensic evidence is as good as any other evidence adduced in a court of law.... The "Homicide, Forensic Science and Criminal Justice System" paper analyses what drives a person to commit a homicide, the prevalence of homicide crimes perpetrated by both genders, the interrelation of government agencies in investigations, and the roles of the police in arresting a perpetrator....
28 Pages
(7000 words)
Coursework
Defining of Health and Safety Violations
The paper ЄDefining of Health and Safety Violations" aims at defining violations, identifying the significance of violations, the reasons why violations occur, the different types of violations, and how violations can be prevented from occurring (Reason, p.... 4).... ... ... ... Within the past 10-15 years, there has been an increased interest in the issues of safety within the workplace....
38 Pages
(9500 words)
Term Paper
Analysing the Handwriting to Expect the Writer's Gender and the Age
investigating the script that helps the experts to recognize the features in the writing and their interaction (Found & Ganas, 2013).... "Analysing the Handwriting to Expect the Writer's Gender and the Age" paper focuses on analyzing handwriting through scientific means to help experts to identify a criminal based on novel features....
54 Pages
(13500 words)
Thesis
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the lab report on your topic
"Investigating the Hookes law by Determining the Spring Constant"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY