StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Health Sciences & Medicine
- The Immunohistochemical Method
Free
The Immunohistochemical Method - Essay Example
Summary
This paper 'The Immunohistochemical Method' tells that A malignant tumor that is derived from the hepatocytes is called hepatocellular carcinoma. This cancer is mainly caused due to viral infections, dietary aflatoxins, and alcohol abuse.The HCC is mainly caused due to the pastor of the Liberations…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER98.5% of users find it useful
- Subject: Health Sciences & Medicine
- Type: Essay
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: ohahn
Extract of sample "The Immunohistochemical Method"
Immunohistochemical method to identify Hepatocellular carcinoma A malignant tumor that is derived from the hepatocytes is called as hepatocellular carcinoma. This cancer is mainly caused due to the viral infections (Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C), dietary alfotoxins and alcohol abuse. The Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is more dominant in China and African countries and is less in USA and European countries (Habib 2000). In China HCC dominancy are due to the presence of high risk populations. In Africa, it is due to the intake of alfotoxins along with the food whereas in Western Countries, it is due to the chronic alcohol abuse. The HCC is mainly caused due to the past history of the Liver infections. Some other symptoms of HCC include abdominal pain, weight loss, malaise, nausea etc. The main symptoms of this disease are hepatomegaly, jaundice, fever, ascites and splenomegaly. The laboratory findings say that the enzyme called as aspartate amino trans-ferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase(ALT), alkaline phosphatase (AP),gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase (GGT),and bilirubin are found in elevated levels in the body due to the effects of HCC. Though these enzymes are not HCC specific but significantly raised level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) of > 500 ng/ml, or continuously rising values even if less than 100
ng/ml, strongly suggest HCC. However, not all cases of HCC are associated with AFP elevation, and raised AFP may also be found in liver disease without HCC. The AFP acts as a marker for the identification of the HCC in our body in the later stages. The second important HCC marker enzyme is des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (DCP). (Hamilton and Aaltonen, 1999).
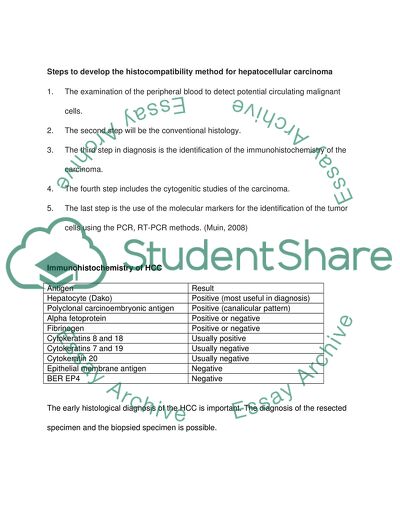
Steps to develop the histocompatibility method for hepatocellular carcinoma
1. The examination of the peripheral blood to detect potential circulating malignant cells.
2. The second step will be the conventional histology.
3. The third step in diagnosis is the identification of the immunohistochemistry of the carcinoma.
4. The fourth step includes the cytogenitic studies of the carcinoma.
5. The last step is the use of the molecular markers for the identification of the tumor cells using the PCR, RT-PCR methods. (Muin, 2008)
Immunohistochemistry of HCC
Antigen
Result
Hepatocyte (Dako)
Positive (most useful in diagnosis)
Polyclonal carcinoembryonic antigen
Positive (canalicular pattern)
Alpha fetoprotein
Positive or negative
Fibrinogen
Positive or negative
Cytokeratins 8 and 18
Usually positive
Cytokeratins 7 and 19
Usually negative
Cytokeratin 20
Usually negative
Epithelial membrane antigen
Negative
BER EP4
Negative
The early histological diagnosis of the HCC is important. The diagnosis of the resected specimen and the biopsied specimen is possible.
Histological Diagnosis of the Resected Specimen:
The tumor cells are known for their intensive growth in all the layers of the tissue, hence this stromal invasion into the fibrous septa, portal tracts, blood vessels must be evacuated carefully. The stromal invasion is classified into three types:
crossing, longitudinal, and irregular. This stromal invasion can be easily detected by the microscopic view or the panoramic view of the specimen. When dissecting the tissue the following things are to be noted out. They are:
1. The amount of the fibrous content of the stroma.
2. Destruction of the structure of the portal tracts.
3. Loss of reticulin fibers around cancer cells.
4. Cytokeratin 7 immunostaining for ductular proliferation. (Kondo, 2009)
Histological Diagnosis of early HCCS of biopsed specimens:
The biopsy diagnosis is a very difficult process than other methods. As the amount of the biopsed material is small, we cannot go for the stromal invasions. This results in the reduction of the results. Only if the parenchymal typia is definite, we can go for the diagnosis. The parenchymal typia includes 1. Nuclear crowding (Hypercellularity). 2. Hyperstainability of cytoplasm (increased concentration of the basophilia or eosinophilia). 3. Microacinar Formation.
Another remarkable change that can be observed is the fatty acid changes.
On the whole the HCC diagnosis is a very difficult process, hence a total overview and summary
Table 1: The various cases of differentiation and the points of differentiation in each case. (Fukuo, 2009)
Various difficult cases
Points of differentiation
1. Dysplastic nodules
Difficult to diagnose definitively by biopsy
If resected or autopsied specimen shows parenchymal atypia as intermediate features between benign liver tissue and well differentiated HCC and no stromal invasion, a definitive diagnosis is made
2. Very well differentiated HCCs
Difficult to diagnose definitively by biopsy
If resected or autopsied specimen shows stromal invasion, a definitive diagnosis is made
3. Large regenerative nodules with high cellularity
Difficult to diagnose definitively by biopsy
However, comparison with extra-nodular control tissue is sometimes useful. In such cases, control tissue also shows high cellularity to some extent
4. Mixture of HCC cells and benign cells
Difficult to diagnose definitively by biopsy
Careful examination is necessary in resected or autopsied specimens
5. Well differentiated HCCs with marked fatty change
Tumor tissue without fatty change should be searched. If this tissue shows the features of well differentiated HCC (hypercellularity double of that in control tissue), a definitive diagnosis is made
6. Benign large regenerative nodules with marked fatty change
Nodule tissue without fatty change should be searched. If this tissue shows the same features as control tissue, the diagnosis is benign liver tissue (a large regenerative nodule or sampling error)
7. Thick sliced specimens with high cellularity and strong stainability of cytoplasm
Specimens must be processed carefully. Nodule tissue and control tissue must be sliced at the same thickness and stained with the same conditions
8. Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) with high cellularity and microacinar formation
Difficult to diagnose definitively only by biopsy
However, a comprehensive evaluation of biopsy specimens and imaging findings is very useful
Figure 1: The Developmental stage of HCC: (Fukuo, 2009)
Figure 2: Stages of chronic liver diseases (chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis) and histological specimens (biopsy, resection, autopsy, and transplantation).
Markers for HCC:
The commonly used markers are HEP Par I (Hepatocyte Antigen), Glypician- 3, Polyclonal Carcinoembryonic Antigen and MOC-31. The less commonly used antibodies include CD10, villin, alpha – Fetoprotein, Transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) , Cytokeratins and CD 34. (Kakar et al, 2007). The Guidelines that are planned for the specific clinical situations are as follows:
1. If the HCC is along with Adenocarcinoma , the foloowing type of combination is used.
a) Hep Par 1 diffuse positive, MOC-31 negative.
b) Hep Par 1 negative, MOC-31 diffuse positive.
c) Hep Par 1 positive, MOC-31 positive.
d) Hep Par 1 negative, MOC-31 negative.
2. If HCC is seen with Chloangiocarcinoma then CK 7 and CK 19 are diffusively positive for cholangiocarcinoma and is usually negative or weakly positive for HCC.
3. The presence of tumors with polygonal cells and HCC are identified by the large tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and round nuclei. For the neuroendocrine tumors MOC-31 is usually positive and CD56 marker is used for the identification.
4. The renal cell carcinoma associated with HCC shows negative results for the Hep Par 1 and p-CEA.
References:
Habib, NA. (2000). Hepatocellular carcinoma, methods and protocols. Humana Press.
Hamilton, SR and Aaltonen, LA. (1999). Pathology and Genetics of the Tumors of the
digestive System. Lyon, France: IARC Press.
Kakar, S et al. (2007). Best Practices in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry: Hepatocellular Carcinoma Versus Metastatic Neoplasms. Archives of Pathology and
Laboratory Medicine. 131, (11): 1648–1654
Kondo, F. (2009). Histological features of early hepatocellular carcinomas and their
developmental process: for daily practical clinical application. Hepatol Int. 3(1): 283–293
Muin, SA. (2008). Phenotypic and genotypic diagnosis of Malignancies. Introduction to
immunohistochemical and molecular methods in tumor Diagnosis, and the
detection of micro metastases and circulating tumor cells. Retrieved November
23, 2009.
http://www.wiley-vch.de/books/sample/352731881X_c01.pdf
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF The Immunohistochemical Method
Small Cell Carcinoma Tumors
The small cell carcinoma tumors are diagnosed by a number of methods, including, electron microscopy, immunohistochemical method, and histochemical method.... From the paper "Small Cell Carcinoma Tumors" it is clear that patients of ages higher than 65 years, at high TNM stage, with metastatic disease at presentation have a poor survival rate....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Research Paper
Ductal cell adenocarcinoma of the breast
The best screening method for DCIS is mammogram only.... Ductal cell adenocarcinoma of the breast Ductal carcinoma In situ (DCIS) is the common type of cancer that is found in the lactiferous ducts of the breast.... This carcinoma starts at the lining of the ducts and then spreads to throughout the lining....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Research Paper
Historical and Clinical Importance of the Sevier Munger Stain
The Sevier-Munger staining method is essentially applied in microscopy to improve visibility in the microscopic picture.... The Sevier-Munger method for argyrophilic discriminatingly stains a small unit of EC cells and ECL cells.... Because the comparative percentage of EC cells stained by Sevier-Munger is insignificant, the method is presently considered essentially definite for ECL cells in paraffin-implanted, formalin-fixed tissues prepared for light microscopy....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Research Paper
Histopathological Examination
One method of obtaining tissue samples from the patient is the use of a minimally invasive procedure called fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy, along with an imaging modality such as ultrasound, MRI scan, or CT scan by the laboratory technician to increase the specificity of locating the mass or lesions in the abdominal area properly (Wee, 2011).... Using this method instead of making an incision in the abdomen of the patient ensures that there would be lesser contaminants entering the samples, and the patient would not worry about excessive bleeding, under normal circumstances....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Essay
Immunohistochemical Method to Identify Epstein Barr Virus in Tonsil Tissue
The paper "immunohistochemical method to Identify Epstein Barr Virus in Tonsil Tissue" discusses that one of the most widespread human viruses, which expanded worldwide during human lives is a virus of the herpes family, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), also called Human herpesvirus 4.... ....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Essay
Immunohistochemical method for identification of ebstein barr virus from the tonsil tissue
immunohistochemical method FOR IDENTIFICATION OF EBSTEIN BARR VIRUS FROM THE TONSIL TISSUEINTRODUCTION: Epstein Barr Virus, commonly referred to as ‘EBV' belongs to the herpes virus family.... This essay describes an immune-histo-chemical method for the identification of Epstein Barr Virus from the tonsil tissue removed from a patient.... This essay describes an immune-histo-chemical method for the identification of Epstein Barr Virus from the tonsil tissue removed from a patient....
2 Pages
(500 words)
Essay
The Gene Expression of Cyclin D
The paper "The Gene Expression of Cyclin D" tells that the gene expression of cyclin D1 in the given breast tumour and normal tissue specimens at mRNA level using semi-quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis techniques.... ... ... ... The technique allows an mRNA molecule to be amplified as complementary DNA (cDNA) copies....
11 Pages
(2750 words)
Lab Report
Preserving Macromolecules in the Field
This method provides excellent specimen integrity and a wide array of options for tissue analysis, including extraction of proteins, DNA, and RNA for use in research and diagnostics.... The idea of this paper "Preserving Macromolecules in the Field" emerged from the author's interest and fascination in how effective is Novel zinc-based fixative (Z7) as a cheap alternative media for preserving specimens (macromolecules) in the field....
10 Pages
(2500 words)
Research Proposal
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the essay on your topic
"The Immunohistochemical Method"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY