StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Education
- The Neuroscience of Learning
Free
The Neuroscience of Learning - Literature review Example
Summary
This literature review "The Neuroscience of Learning" presents the neurophysiologic basis of learning that is vital for all to understand. Many advances in this field have been made recently, but scientists have not learned everything about how the brain works…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER96.1% of users find it useful
- Subject: Education
- Type: Literature review
- Level: Masters
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: flatleydestany
Extract of sample "The Neuroscience of Learning"
Neurobiology The topic on neurobiology chosen for this paper is on the article The neuroscience of learning. Learning is more complicated than justnurture and teaching. The neurophysiologic basis of learning is important for doctors and nurses to understand. Many advances in this field have been made recently. The more that is learned about the neurophysiologic, the more diverse teaching methods can be used for individuals with normal brain activity and brain damaged individuals. The theory of multiple intelligences, as it concerns neurophysiologic, is also explored in this article. Some experts agree, while others disagree. This article asserts that nurses are in the position to use neurophysiologic concepts in order to educate patients in a more efficient manner.
Today the neuroscience of learning is far from complete. Scientists are getting answers to some questions, but the brain still remains a mystery to be studied. What has been learned is long-term memory have the aspects of “Long-term potentiation (LTP) and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) responsive element binding (CREB protein activation” (Collins, 2007). Mirror neurons are essential in learning action tasks (Collins, 2007). Finally, Gardner (1983) identified that different portions of the brain are responsible for different learning abilities.
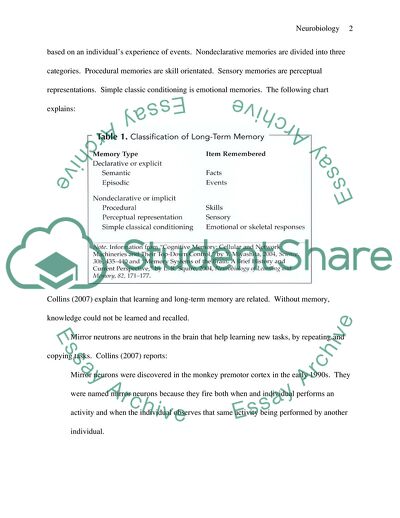
Memory classification is essential to understanding how the brain learns and processes information. Short-term memory and long-term memory are two of the more common terms used when classifying memory. Long term memory consists of declarative and nondeclarative forms. This can be broken down further into semantic memory and episodic memory (Miyashita; 2004). Semantic and episodic memories are located in the hippocampus in the medial temporal lobe (Squire, 2004). Semantic memories are fact based. Episodic memories are based on an individual’s experience of events. Nondeclarative memories are divided into three categories. Procedural memories are skill orientated. Sensory memories are perceptual representations. Simple classic conditioning is emotional memories. The following chart explains:
Collins (2007) explain that learning and long-term memory are related. Without memory, knowledge could not be learned and recalled.
Mirror neutrons are neutrons in the brain that help learning new tasks, by repeating and copying tasks. Collins (2007) reports:
Mirror neurons were discovered in the monkey premotor cortex in the early 1990s. They were named mirror neurons because they fire both when and individual performs an activity and when the individual observes that same activity being performed by another individual.
These mirror neurons help the brain by not only repeating tasks, but also by observing the task that is being learned.
Collins (2007) reveals that Hebb rule, LTP and CREB protein are related to learning. Short-term memories must be turned into long-term memories. A structural change must occur within neurons for this process to happen (Collins, 2007). The Hebb rule bolsters this argument:
Let us assume that the persistence or repetition of a reverberatory activity (or ‘trace’) tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability.… When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that As efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased. (Hebb, 1949)
Hebb’s rule was first noticed in the LTP. Another hypothesis is that “a cAMP second messenger system with protein phosphatases determines when LTP can occur at synapses” (Collins, 2007). This however is unknown, only speculated at this time.
Finally, Gardner (1983) asserts that “different areas of the brain are responsible for different competencies.” The following chart shows the different competencies that Gardner found:
The problem with Gardner’s theory is that he has been unable to identify which parts of the brain are responsible for each learning area. Some areas of Gardner’s intelligence overlap in cognitive parts of the brain (Klein, 1997).
Collins’ article tries to tie in the benefits of learning neuroscience to nursing. This can be helpful in not only teaching fellow nurses, patient’s families, and patients. It has been noticed that different individuals learn differently. Some people learn by sight, others by hearing, and yet others by a hands on method. When further research can be done into how the brain neurologically processes memory and learning, then teaching will become easier. This will benefit nurses by allowing them to effectively train fellow nurses. Since teaching a patient’s family about aftercare is important, nurses could teach patient’s families on how to better treat their loved ones. Finally, patients with brain injuries can be retrained to have fulfilling lives. If that is not possible, at least nurses can teach caregivers what to expect. This allows caregivers to understand and be less frustrated with brain injury patients, by allowing them to know what to expect. Collins (2007) explains:
Because practice and repetition are major factors in committing information to long-term memory, important material needs to be repeated and emphasized. Neuroscience teaches us several ways that material can be emphasized. A powerful technique is to build on existing learning networks. This approach incorporates new learning experiences into existing long-term memory.
Nurses can take the knowledge and help patients and others learn in unique ways. An example would be a person that learns by repeating a task using the mirror neurons could be taught by a nurse how to complete a task by repetition.
Collins wrote a good article, but the ending was not expansive enough. There were no references on the last page, only speculation. It would have been better to either elaborate about nurses and neuroscience learning or not to include the part about nurses or patient care at all. If I would have written the article, I would have elaborated on examples of nurses and patient interaction, which would also include other studies. If more research would have been done on nurses, patients, especially brain damaged patients, and a patient’s family would have made this paper much better.
On the other hand, this article was very informative on neuroscience of learning. It showed where memory neuroscience is today and how it affects learning. Classification of memory, Mirror Neurons, the Hebb rule, LTP, and CREB proteins were all explained. The lack of information, like which parts of the brain are affected by the classification of memory was due to the process of science, not the author’s lack of research. This area was explored fully by the author.
The summary was not satisfactory. It was too short. Plus the summary focused on the nurses’ role in neuroscience and learning. The majority of the paper had to do with the neuroscience of learning, not the nurses’ role or patient education. I would have created a better conclusion that encompassed my whole paper entirely.
The neurophysiologic basis of learning is vital for all to understand. Many advances in this field have been made recently, but scientists have not learned everything about how the brain works. The more that is learned about the neurophysiologic, the more diverse teaching methods can be used for individuals with and without brain damaged. Nurses can learn from neurophysiologic sciences to help patients and their families. Over all Collins’ article was informative and based on the current knowledge of the neuroscience of learning.
References
Collins, J.W. (2007). The neuroscience of learning. Continuing Education, 39(5), 305-310.
Gardner, H. (1983). Frames of mind: The theory of multiple intelligences. New York: Basic
Books.
Gardner, H. (1999). Intelligence reframed: Multiple intelligences for the 21st century. New
York: Basic Books.
Hebb, D.O. (1949). The organization of behavior. New York: Wiley.
Klein, R.M. (1999). The Hebb legacy. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology, 53, 1-3.
Miyashita, Y. (2004). Cognitive memory: Cellular and network machineries and their top-down
control. Science, 306, 435-440.
Squire, L.R. (2004). Memory systems of the brain: A brief history and current perspective.
Neurobiology of learning and Memory, 82, 171-177.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF The Neuroscience of Learning
Cognitive Neuroscience
Some of the major advancements have been in the field of cognitive neuroscience which has been widely studied and has come to be used in many fields.... Cognitive neuroscience has mainly been used to explain the different aspects of human behavior.... ognitive neuroscience is a concerned with the scientific study of the biological substrates that are known to underlie cognition.... The focus in cognitive neuroscience is on the neural substrates concerned with the mental processes....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Essay
Sigmund Freud Contributions in Psychoanalysis and Neuroscience
The researcher of this descriptive essay mostly focuses on the discussion of the topic of Sigmund Freud's undisputed contributions in theory of Psychoanalysis and in the modern neuroscience and analyzing this issue in the broad historical overview.... In this profound research essay the author analyses major concepts of Sigmund Freud theory and his contribution to Psychology and modern neuroscience.... The essay "Sigmund Freud Contributions in Psychoanalysis and neuroscience" is a profound research paper analysing the contribution of the great psychologist Sigmund Freud....
10 Pages
(2500 words)
Research Paper
The Future of Nursing, Leading Change, Advancing Health
It is also crucial that AANN reflect on supporting options comprising degree and non-degree courses, fellowships, and institutions that promote the education and support lasting learning of neuroscience nurses (IOM, 2010).... neuroscience nurses must be able to carry out their duties to the fullness of their training and education training despite their posting whether bedside nurses or advanced practitioners in the community (IOM, 2010).... For this cause, the American Association of neuroscience Nurses (AANN) tactical plan commissioned a task force to revise its 2002 scope and standards article....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Essay
The Role of the Amygdala in Fear Processing
In terms of fear and its causes, the search for an exact definition entails a level of uncertainty amongst neuroscience researchers.... The report "The Role of the Amygdala in Fear Processing" focuses on the essence of fear and the advancement of coping with it within our brain.... ...
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Report
Current and Future Applicaitons
Developments in the area of lifelong learning, ageing, education, mental disorders and other aspects of neuroscience will all affect the way psychologists.... Developments in the area of lifelong learning, ageing, education, mental disorders and other aspects of neuroscience will all affect the way psychologists approach various issues that they face regarding the analysis and interpretation of activities in the human brain.... One area where psychologists, as well as educators and academicians will have to modify their methods is in the latest findings on the optimal timing or “sensitive periods” when the capacity to learn is greatest in areas such as language learning (Centre for Educational Research and Innovation 11)....
1 Pages
(250 words)
Assignment
Cognitive Psychology and Neuroscience in Learning Process
The paper "Cognitive Psychology and Neuroscience in learning Process" argues in a well-organized manner that professor Oakley describes ten rules for studying well.... The ability to recall generates ideas from the inside, hence indicating good learning.... The fourth rule is to space one's repetition by spreading out the learning a little every day in any subject.... Professor Oakley, in her text, provided practical and far-reaching insight from cognitive psychology and neuroscience from the practical teaching of University level courses that are tough when taught....
1 Pages
(250 words)
Essay
Neuroscience and Identity Theory
The paper "neuroscience and Identity Theory" explores whether psychotherapists inform patients that they are suffering from "chemical imbalances" or from "unresolved developmental traumas".... neuroscience is founded on a philosophy of mind known as identity theory.... The current philosophy of mind, both stimulated and rejuvenated by neuroscience research, is in fast pursuit of a comprehensive mind/brain theory.... neuroscience has a conceptual foundation that is based on an incomplete theory of mind and brain: identity theory....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Essay
Cognitive Neuroscience
This coursework "Cognitive neuroscience" aims to disprove this by identifying the different approaches with which cognitive neural science can be used to explain human behavior, and how it can be applied to the understanding of the different ways in which people believe.... Cognitive neuroscience is important as it helps in the creation of an understanding of the neural basis of human behavior.... Some of the major advancements have been in the field of cognitive neuroscience which has been widely studied and has come to be used in many fields....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Coursework
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the literature review on your topic
"The Neuroscience of Learning"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY