StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Physics
- Applications of AC Theory
Free
Applications of AC Theory - Lab Report Example
Summary
The paper "Applications of AC Theory" highlights that the alternating current theory is quite applicable in solving many problems in electrical engineering. AC theory is therefore applicable in Radios, transformers, audio devices such as hi-fis, and loudspeakers…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER91.5% of users find it useful
- Subject: Physics
- Type: Lab Report
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: delldeckow
Extract of sample "Applications of AC Theory"
September 7, APPLICATIONS OF AC THEORY INTRODUCTIONS A waveform which varies in time is called AC, it also knownas a sinusoidal waveform. The polarity of an AC waveform changes from a positive value to a negative value of the variable applied. An AC waveform is time-dependent and is usually a product of a rotating generator. The shape of this periodic waveform is obtained by using a fundamental frequency and adding harmonic signals for varying amplitudes and frequencies. The main characteristics of AC waveforms are:
PERIOD (T): It is also called periodic time and is the time it takes a periodic wave to move from positive to negative value, and in square waves it is referred as pulse width.
THE FREQUENCY (f): This is the number of times a waveform repeats itself in a unit time period, and is given as the reciprocal of time period and given in Hertz (HZ).This implies that, f=1/T.
AMLITUDE (A) : Magnitude the AC signal and is measured in Amps or Volts.
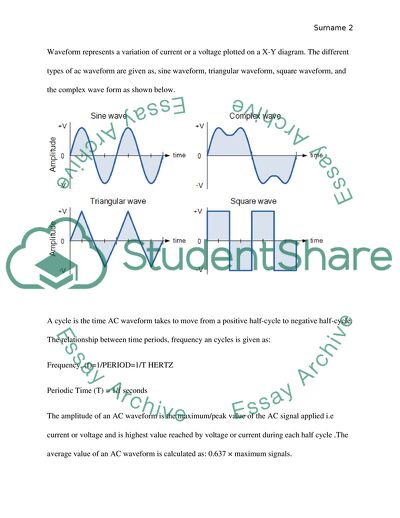
Waveform represents a variation of current or a voltage plotted on a X-Y diagram. The different types of ac waveform are given as, sine waveform, triangular waveform, square waveform, and the complex wave form as shown below.
A cycle is the time AC waveform takes to move from a positive half-cycle to negative half-cycle. The relationship between time periods, frequency an cycles is given as:
Frequency, (f)=1/PERIOD=1/T HERTZ
Periodic Time (T) = 1/f seconds
The amplitude of an AC waveform is the maximum/peak value of the AC signal applied i.e current or voltage and is highest value reached by voltage or current during each half cycle .The average value of an AC waveform is calculated as: 0.637 × maximum signals.
The RMS Value of an AC waveform is the defined as the equivalent mean value of an AC system that gives to the load the same power as the same DC circuit, and is calculated as:
RMS VALUE=0.707×Vpp/Ipp.
Form factor is the ratio of RMS value to the mean value and it determines the shape of the waveform.
Different applications of AC theory are as follows
1) PRODUCTION OF WAVEFORMS:
Square waveform:
RMS value =peak value of current or voltage
Saw tooth waveform: The saw tooth wave form has an RMS=0.577×Vpp/ Vpp, The mean value for a saw tooth is 0.5×peak value and the form factor is given as 1.11.
Sine wave: The RMS value of a sine wave is given 0.707×(peak value) and the average value is given as 0.636×(peak value) hence the form factor of sine wave is 1.15.
Harmonics are usually developed in AC power systems when AC is rectified to DC and is usually done by use of diodes, or bridge rectifiers
2) DETERMINING THE SHAPE OF DIFFERENT WAVEFORMS
Q1) given the following waveform equation
v = DC + V1sin (t + ϴ1)+ V2sin (2t + ϴ2)+ V3sin (3t + ϴ3) + … Volts
i) Saw tooth waveform
V rms =O.577×100=57
V mean=0.5×100=50V
Form factor=1.15
DC=50V,
Hence v=50+100sin(t)+33.33sin(2t + 45)+20sin(3t + 90)+14.29sin(3t + 135)+….
ii) Square wave
V rms=100V, mean voltage=100V and form factor=1
Hence v=100+100sin(t)+33.33sin(2t + 45)+20sin(3t + 90)+14.29sin(3t + 135)+…
iii) Sine wave
Rms voltage=0.707×100=70.7V, mean voltage=0.636×100=63.6V Hence form factor=1.11
V=63.6+100sin(t)+33.33sin(2t45)+20sin(3t +90)+14.29sin(3t +135)+…
Simulation of the waves produced above was done by use of a 10 ohms resister and it was clear that the equations obtained above were correct.
1) 2) A complex voltage is determined by: v = 120sint + 19sin (3t + 40) + 8.5sin (5t - 65) Volts. Where the frequency is 60Hz.Use Microsoft Excel (or something similar) to plot two complete cycles of the above waveform (show the fundamental and harmonic components as well as the overall waveform on the same graph).
The fundamental harmonic originates from Zero while third harmonic sine wave leads the first harmonic by 40 degrees and the fifth harmonic lags by 65 degrees.
3) Voltage of: v = 115sint + 39sin (3t + 60) + 11.5sin (5t - 15) Volts
(Assume the frequency to be the 50Hz) is applied to the terminals of the circuit below.
a) Find the value of the capacitor to make the above series circuit resonate at the third harmonic frequency.
During the third harmonic f=150HZ
B f=
C=9.8mF
b) Using the value of capacitance found in a) above, find an expression for the instantaneous current. In the form i = If sin (t + ) + I3sin(3t +) + I5sin(5t + ) amps
Reactance X=Xc+ XL
X=349.70 ohms
Z=352.90ohms
I peak=V peak/Z Hence, I first harmonic=.0.3A,second harmonic=0.1A,Third harmonic=0.03A hence i=0.3sin((t + )+0.1sin(3t +) +0.03sin(5t + ) amps
c) Using the answer to b) above, find the RMS value of this current.
I=-0.21+-0.07+0.02=0.16A
I rms=0.113A
4) The circuit shown below is for a typical fluorescent lamp fitting, which is connected to a 230V 50Hz supply. Assuming the fluorescent tube has an operating resistance of 95Ω, calculate:
a. the impedance of the circuit
Impendence (Z)=
F=50HZ
L=520mH=0.52H
C=11mF=0.000011F
R=r+Rf =14+95=109 Rf is the resistance of the fluorescent.
V peak=230V
XC==289.86r Where Xc is the reactance due to the capacitor C
XL=2pifL=163 Where XL is the reactance due to the inductor L
X==372 ohms Where X is the total reactance due to capacitor C and Inductor L.
Z=388.06 ohms.Where Z is the total impendence of the circuit due to presence the reactance and resistance.
b. the current flowing through the tube
Current (I) =
V peak=230
This implies that I=0.59Amps
c. the power dissipated by the tube
Power=IZ=136.32 watts
d. the operating phase angle () of the complete fitting
angle=tan=73.67
e. the supply current to the fitting
I rms=V rms/Z=0.42Amps
5) In the following ideal transformer a turns ratio of 12:1, calculate:
Maximum power occurs when, ()= Where Rl is the load resistance and Rs is the resistance in series with the supply voltage of the transformer. Hence
Load resistance Rl=11.1 ohms where Rs=1600 ohms
Input impendence (Zp )= ()× Rl=1600 ohms
Load Voltage (V2)=×V1=19.17V RMS
Power developed (p)=V2/Rl=33.08 W
6) A 25 resistor is connected to the secondary winding of a ‘perfect’ single phase transformer. The terminal voltage at the secondary is 230V. If the Primary terminal voltage is 1000V, calculate:
f. The turn’s ratio.
This implies that turns ratio is given as, the ratio of the primary and a secondary voltage which is 100:23, Where N1 and N2 are primary and secondary voltages respectively while V1 and V2 are primary and secondary voltages.
g. The current I2 (A) and power P2 (W) drawn by the load.
V rms=Vpeak×0.707=230×0.707=162.61
I rms=V rms/Rl=6.50A
Power=I rms×R
=1057.68 W
h. The current drawn from the supply I1 (A)
V rms=Vpeak×0.707
=1000×0.707=707V
I rms= V rms/Rp but Rp=472.59ohms Hence I=1.5Amps
Where Rp is the resistance at the transformer input
i. State the losses found in a typical transformer.
Winding losses which occurs when heating occurs as a result of winding resistance which leads to loss of energy inform of heat in the windings. Winding losses is also referred to as copper losses since most of transformer windings are made of copper.
CORE LOSSES
Core losses are sub-divided into:
Hysteresis
Eddy current losses
CONCLUSION
It was found out that the alternating current theory is quite applicable in solving many problems in electrical engineering. AC theory is therefore applicable in Radios, transformers, audio devices such hi-fis, and loudspeakers.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Applications of AC Theory
Principles of Economics
The purpose of this paper is to answer questions pertaining to macro-economic and micro-economic theory.... Principles of Economics Assignment The purpose of this paper is to answer questions pertaining to macro-economic and micro-economic theory.... The format that this paper will utilize is to first directly outline the question and then provide a critical response based on relevant literature....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Essay
The Theory of Reasoned Action
This essay "The theory of Reasoned Action" talks about according to the behaviour of individuals can be influenced by their intention of performing a certain behaviour.... The theory of Reasoned Action in the Case of Aldi Review of Related Literature theory of Reasoned Action According to the theory of reasoned action, the behaviour of individuals can be influenced by their intention of performing a certain behaviour.... The application of the theory of reasoned action in various studies has shown the relevance of each of the variables as explained by the model....
12 Pages
(3000 words)
Essay
The Theory of Probability by Blaise Pascal
The paper "The theory of Probability by Blaise Pascal" tells that the analysis of the gambling laid foundation for more complicated logic and mathematical probability.... The Importance and Application of theory of Probability The theory of Probability by Blaise Pascal served humanity for centuries until the present.... The Importance and Application of theory of Probability Introduction Mathematics has helped people in quantifying things as the numerals offer the convenience of calculating objects....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Research Paper
Theory of the experiment
The aim of the paper 'theory of the experiment' is to build an amplifier; to evaluate the performance of the built amplifier; to learn the functions of its components through testing; to improve my knowledge and skills of an amplifier through conducting 'real' experiments.... theory of the experiment
... he DC and ac components of the signal were measured.
... he voltage Vb (Total) and Vb (ac).
... b (total) was measured and Vb (ac).
...
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Lab Report
System Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
The paper "System Security Threats and Vulnerabilities" describes that the web-based service would be achieved through distributed interactivity.... SOA, distributed infrastructure, and business process management (BPM) would be integrated for achieving meaningful and collaborative learning processes....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Assignment
COMSOL Multiphysics
This confirms the theory that states that the electric field moves from high charges to low charges in lines.
... owever, in this report we have a typical electrode geometry used to extract biological cells from a sample using the ac electrokinetic process known as dielectrophoresis.... We need, as mentioned before, to calculate the electric field and the electric potential for figure 3, which is a typical electrode geometry used to extract biological cells from a sample using the ac electrokinetic process known as dielectrophoresis....
10 Pages
(2500 words)
Research Proposal
Alternating Current Theory in Use
September 7, Applications of AC Theory INTRODUCTION Alternating current (AC) refers to a waveform which varies in time, also referred to as a sinusoidal waveform.... ifferent Applications of AC Theory are as follows
... The different waveforms produced by use of ac theory are:
... ) ac theory is used to recognize a variety of complex waveforms and also it is used to these waveforms are produced.... ac theory is therefore applicable in Radios, transformers, audio devices such hi-fis, and loudspeakers.
...
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Math Problem
Information Security Standards
elevance of planning theory to security planning 23
... Here we have Protect, Detect and React theory.... elevance of planning theory to security planning
... n case of the TRANSCORP Transport Company relevance of planning theory to security planning is having garter means....
11 Pages
(2750 words)
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the lab report on your topic
"Applications of AC Theory"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY