StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Nursing
- Hand Hygiene: A Frequently Missed Lifesaving Opportunity during Patient Care
Free
Hand Hygiene: A Frequently Missed Lifesaving Opportunity during Patient Care - Term Paper Example
Summary
For this study, the guidelines on proper hand washing and the use of alcohol-based hand gels as suggested by the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are provided followed by conducting a short literature review to prove that hand hygiene is a frequently missed lifesaving opportunity …
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER98.1% of users find it useful
- Subject: Nursing
- Type: Term Paper
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 1
- Author: bbernhard
Extract of sample "Hand Hygiene: A Frequently Missed Lifesaving Opportunity during Patient Care"
Hand Hygiene: A Frequently Missed Lifesaving Opportunity during Patient Care
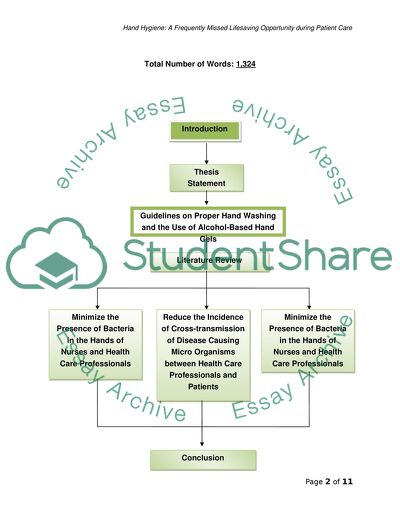
Table of Contents
I. Introduction ……………………………………………………………… 4
II. Thesis Statement ……………………………………………………….. 4
III. Guidelines on Proper Hand Washing and the Use of
Alcohol-Based Hand Gels ……………………………………………... 5
IV. Literature Review ………………………………………………………. 6
a. Minimize the Presence of Bacteria in the Hands of
Nurses and Health Care Professionals …………………. 6
b. Reduce the Incidence of Cross-transmission of
Disease Causing Micro Organisms between
Health Care Professionals and Patients ………………… 6
c. Decrease the Number of Patients’ with
Healthcare-associated Infections (HAI) …………………. 7
V. Conclusion ……………………………………………………………….. 8
References ……………………………………………………………………….. 9 - 10
Introduction
Hand hygiene or washing the hands with soap is considered to be one of the most effective infection control measures. Despite the importance of hand hygiene, several studies reported that the number of hospital-acquired infection is approximately 1.4 million people all over the worlds (Vincent, 2003; Tikhomirov, 1987).
The main purpose of hand hygiene is to reduce the number of micro organisms that are present on the hands of the nurses and health care professionals. Considering that the job of nurses requires physical contact with the patients when rendering care and treatment, washing hands with soap should be given importance in order to minimize the possibility of transmitting these micro organisms between the health care professionals and the patients (Larson et al., 2005).
For this study, the guidelines on proper hand washing and the use of alcohol-based hand gels as suggested by the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will be provided followed by conducting a short literature review to prove that hand hygiene is a frequently missed lifesaving opportunity when rendering care to patients.
Thesis Statement
Hand hygiene can save the life of the patients since washing hands with anti-microbial soap reduces the following: (1) the presence of bacteria in the hands of the nurses and health care professionals; (2) incidence of cross-transmission of disease causing micro organisms between the health care professionals and patients; and (3) the number of patients’ with healthcare-associated Infections (HAI).
Guidelines on Proper Hand Washing and the Use of Alcohol-Based Hand Gels
Prior to washing hands with soap, nurses and health care professionals should keep their nails short to avoid harboring micro organisms (CDC, 2002: p. 46). Nurses and health care professionals are also required to remove all jewelry before washing the hands to facilitate a better and proper cleaning of hands and arms.
Always gather the necessary equipments needed such as antimicrobial or regular soap, alcohol-based waterless antiseptic, paper towels or dyer, clean orange wood stick (for surgical hand washing) before washing the hands. Gathering all the equipments prior to hand washing will save more time for nurses and health care professionals. In case of skin cuts or wounds, nurses and health care professionals should cover it first after hand washing before going to a client. This way, his/her wound will not get infected with bacteria, viruses, and other micro organisms.
When washing the hands, make sure to keep wet hands and wrists under running water. Always keep hands and forearms lower than the elbow during hand washing so as to avoid contaminating the clean upper part of the arms. After wetting the hands, start applying a small amount of antimicrobial soap and lather thoroughly for 10 to 15 seconds followed by drying hands using paper towel, single-use cloth, or warm air drier (CDC, 2002b).
When using alcohol-based hand gels, applying a small amount of gel on palm and rub hands together until the gel covers the entire surface of the hands and fingers. Rubbing of hands should be done for several seconds until the alcohol becomes dry. (Kampf, 2004)
Literature Review
Minimize the Presence of Bacteria in the Hands of Nurses and Health Care Professionals
Nurses and health care professionals’ hands are capable of collecting a thousand units/cm2 of micro organisms. (Selwyn, 2000) Based on the study of Lijima and Ohzeki (2006) which measured bacterial contamination on the nurses’ hands after patient care, the authors revealed that the practice of proper hand hygiene can significantly lessen the amount of bacteria present on the hands of the nurses.
Upon examining the effects of using the usual hand washing using anti-microbial soap and waterless-alcohol hand gels, Larson et al. (2005) concluded that the use of both techniques is both effective in terms of preventing possible infection as well as the number of micro organisms that were found on the hands of the nurses. On the contrary, Widmer (2000) concludes that the use of ‘alcohol-based cleanser’ is not only so much easier to use but also more effective in terms of lowering down the number of micro organisms as compared to the traditional hand washing routine.
Reduce the Incidence of Cross-transmission of Disease Causing Micro Organisms between Health Care Professionals and Patients
The hands of the health care professionals can easily transmit micro organism from one place to another. (Simon, 2004) For this reason, several studies revealed that making hand hygiene a habit can significantly reduce the number of cases that are related with the transmission of infectious diseases from one patient to another. (Larson, 1999) Aiming to prevent and minimize the possibility of cross-transmitting infectious diseases within the hospital environment, antibacterial soap was intentionally produced to protect the patients who are admitted in hospitals from bacterial, virus, and pathogen infections. (Levy, 2001)
In general, the problem that is often associated with regular hand washing using antiseptics made of detergents is that it can cause the nurses’ skin to get too dry up to the point that is damages and increases the risk of micro organisms transmission. For this reason, Larson (1999) suggest that nurses and health care professionals should consider using other hand hygine options like the ‘waterless alcohol-based products’ instead of using ‘detergent-based antiseptics’ when undergoing surgical scrub requirements. It is also advisable to use of moisturizers to protect their skin from excessive dryness.
Decrease the Number of Patients’ with Healthcare-associated Infections (HAI)
‘Healthcare-associated Infections’ (HAI) is a serious health condition since it extends the patients’ stay at the hospital, increases the hospital bill as well as the patients’ risk of untimely deaths. (Cosgrove, 2006) With regards to HAI, a large number of the health care professionals throughout the United States do not practice hand hygiene regularly. (Larson et al., 2005)
Among the common reason why health care professionals like nurses failed to wash their hands regularly includes the following: (1) nurses and other health care professionals either do not remember or do not have sufficient time to wash their hands before rendering patient care; (2) fear that their skin will become excessively dry and damaged; and (3) the hand rub gel and sinks is located far away from the working area of the health care workers (Pittet et al., 1999). Since it is very seldom that the health care workers will go beyond forty percent of hand washing requirements (Widmer, 2000), Starfield (2000) revealed that “almost one out of every 136 patients or 2 million patients each year are at risk of becoming seriously ill because of healthcare-associated infections (HAI)”. In worst cases, HAI can also lead to the patients’ untimely death.
To effectively prevent the cases of HAI, several studies revealed that the good hand hygiene is the best way to avoid HAI and the control the spread of multi-resistant micro organisms is to clean the health care workers’ hands with ‘alcohol-based hand gel’ for a few seconds before and after providing each patients with care and treatment (Pittet et al., 2006; Hugonnet et al., 2002) Since the use of hand gels basically requires a few seconds as compared with washing the hands using anti-bacterial soap, the study of Hugonnet et al. (2002) suggest that there is a strong possibility that the use of hand rub gels will eventually be a better option that a typical hand washing with soap.
Conclusion
A lot of nurses and health care professionals do not comply with hand hygiene protocol. To control and prevent the possible transmission of disease causing micro organisms from one patient to another, nurses and health care professionals should make it a habit to wash their hands before and after rendering patient care.
With the use of anti-bacterial soap and other preventive control measures like the use of alcohol-based hand gels, it is possible for nurses and health care professionals to save the lives of many patients since proper compliance with the washing hands with soap protocol can effectively minimize the number of cases related to healthcare-associated Infections (HAI) throughout the United States.
References:
CDC. (2002b, October 25). Retrieved September 26, 2008, from Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-Care Settings. Recommendations of the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee and the HICPAC/SHEA/APIC/IDSA Hand Hygiene Task Force. MMWR Recommendations and Reports. 51(RR16):1 - 44 : http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5116a1.htm
CDC. (2002). Nails should always be kept short and filed; Do not wear artificial nails or extenders when providing patient care. CDC Guidelines. Draft Revision of the Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health Care Settings. CDC.
Cosgrove, S. (2006). The relationship between antimicrobial resistance and patient outcomes: mortality, length of hospital stay, and health care costs. Clinical Infectious Diseases , 42(Suppl 2):582 - 589.
Hugonnet, S., Perneger, T., & Pittet, D. (2002). Alcohol-based handrub improves compliance with hand hygiene in intensive care units. Archives of Internal Medicine , 162:1037 - 1043.
Kampf, G. (2004). The six golden rules to improve compliance in hand hygiene. Journal of Hospital Infection , 56(Suppl 2):3 - 5.
Larson, E. (1999). Skin hygiene and infection prevention: more of the same or different approaches? Clnical Infectious Diseases , 29(5):1287 - 1294.
Larson, E., Cimotti, J., Haas, J., et al. (2005). Effect of antiseptic handwashing vs alcohol sanitizer on health care-associated infections in neonatal intensive care units. Archieves of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine , 159(4):377 - 383.
Levy, S. (2001). Antibacterial household products: cause for concern. Emerging Infectious Diseases , 7(3 Suppl):512 - 515.
Lijima, S., & Ohzeki, T. (2006). Bacterial contamination on the hands of nursing staff in the most basic neonatal care. Journal of Neonatal Nursing , 12(2):53 - 55.
Pittet, D., Allegranzi, B., & Sax, H. et al. (2006). Evidence-based model for hand transmission during patient care and the role of improved practices. The Lancet Infectious Diseases , 6(10):641 - 652.
Pittet, D., Mourouga, P., & Perneger, T. (1999). Compliance with handwashing in a teaching hospital. Infection Control Program. Annals of Internal Medicine , 130:126 - 130.
Selwyn, S. (2000). Microbiology and ecology of the human skin. Practitioner , 224:1059 - 1062.
Simon, A. (2004). Hand hygiene, the crusade of the infection control specialist. Alcohol-based handrub: the solution! Acta Clinica Belgica , 59(4):189 - 193.
Starfield, B. (2000). Is US health really the best in the world? Journal of the American Medical Association , 284(4):483–485.
Tikhomirov, E. (1987). WHO Programme for the control of hospital infections. Chemiotherapia , 3:148 - 151.
Vincent, J. (2003). Nosocomial infections in adult intensivecare units. Lancet , 361:2068 - 2077.
Widmer, A. (2000). Replace hand washing with use of a waterless alcohol hand rub? Clinical Infectious Diseases , 31(1):136 -143.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Hand Hygiene: A Frequently Missed Lifesaving Opportunity during Patient Care
The Use of Alcohol Rub in Preventing Infection
Through this, particular circumstances can be known in which alcoholic hand rubs must be used, and instances where it must not be made use of.... The research will provide a brief rationale the current topic was chosen.... This study defines the evidence based practice and its importance to professional practice and then discuss the factors that hinder or facilitate evidence based practice....
9 Pages
(2250 words)
Essay
World Health Organization Guidelines for Hand Hygiene in Health Care
This essay "World Health Organization Guidelines for hand hygiene in Health Care" is about a worldwide need to develop hand hygiene, and was prepared with the help of more than 100 international experts, that are in the testing and implementation phases in different parts of the world.... These international consensus rules reinforce the requirement for multidimensional policies as the most capable process to assist hand hygiene.... 'Key elements include staff education and motivation, adoption of an alcohol-based hand rub as the primary method for hand hygiene, use of performance indicators....
9 Pages
(2250 words)
Essay
Oral Hygiene and Mouth Care
The paper "Oral Hygiene and Mouth care" highlights that oral hygiene and mouth care are related to respiratory illnesses, especially in ICU and seriously ill patients.... Oral care is imperative to promoting a healthy patient, especially in seriously ill, geriatric, and cancer patients.... Good oral hygiene is linked to the prevention of somatological diseases in older residents (Ship 2002), as well as periodontal diseases and infections in diabetic patients (Nursing 1993), and oral care reduces pneumonia in older patients (Yoneyama, 2004)....
16 Pages
(4000 words)
Essay
Effective Hand Hygience
This 'accountability' is usually spelled out in 'patient care Documents' established by hospital associations and medical associations or councils of every country [9].... The idea of this paper "Effective hand hygiene" emerged from the author's interest and fascination with why healthcare professionals in an organization like National Health Service need to follow a recognized protocol to maintain effective hand hygiene.... Changes occurring in Health care delivery and Medicine are the result of social, economical, technological, and scientific forces....
19 Pages
(4750 words)
Essay
Improving Adherence to Hand Hygiene Practice
The Department of Health and Human Services of the United States stressed the needs of using hand gloves on infected patients directing that 'A single pair of patient care gloves should be worn for contact with blood and body fluids, including during hand contact with respiratory secretions (e.... In the paper 'Improving Adherence to hand hygiene Practice' the author discusses the issue that most of the medical practitioners suggests and implies that the majority of the diseases today is being acquired by hand....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Assignment
Hand Hygiene and Infection Control
"hand hygiene and Infection Control" paper analizes five studies in the field of hand hygiene and its usage in preventing infections within hospital settings.... From the analysis of reviewed literature and creating awareness about the harmful effects of bad hand hygiene habits is identified as the best alternative approach available to medical practitioners.... Infection control measures include several sub-fields such as using sterilized hospital equipment, hand hygiene, etc....
16 Pages
(4000 words)
Literature review
Health Policy Analysis on Hand Hygiene
"Health Policy Analysis on hand hygiene" paper argues that the importance of proper hand-washing techniques and protocol is both well-known and misunderstood.... Because of the critical function that hospital and healthcare facility staff play in maintaining a healthy environment for patients, many of whom are already ill or suffering from various types of infection, it has become necessary to implement some type of system to ensure that hands are properly washed before entering into any patient zone....
14 Pages
(3500 words)
Coursework
Factors or Barriers that Influences Adherence to Hand Hygiene among Nurses in Saudi Arabia
The paper "Factors or Barriers that Influences Adherence to hand hygiene among Nurses in Saudi Arabia" is an outstanding example of a term paper on nursing.... hand hygiene (HH) is the best infection control strategy employed to prevent the introduction of harmful microbes into the human body system.... The paper "Factors or Barriers that Influences Adherence to hand hygiene among Nurses in Saudi Arabia" is an outstanding example of a term paper on nursing....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Term Paper
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the term paper on your topic
"Hand Hygiene: A Frequently Missed Lifesaving Opportunity during Patient Care"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY