StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Macro & Microeconomics
- The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand
Free
The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand - Assignment Example
Summary
This paper under the headline 'The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand" focuses on the fact that the essence of business is to satisfy the needs and wants of the consumers profitably and there are many economic factors which affect this process. …
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER93% of users find it useful
- Subject: Macro & Microeconomics
- Type: Assignment
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: lharvey
Extract of sample "The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand"
The essence of business is to satisfy the needs and wants of the consumers profitably and there are many economic factors which affect this process. According to Kotler & Armstrong (2004, p. 6), “Needs are states of felt deprivation while wants are the form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality.” When backed by buying power, wants become demands and the people demand products with benefits that add up to the most value and satisfaction. The law of demand goes hand in hand with price of the product. Thus, before setting the price, the marketer must understand the relationship between the product and its demand. Price-demand relationships vary from different types of the markets and buyer perception. This relationship can be illustrated graphically using demand curves. As such, this essay seeks to describe the differences between shifts in demand and movements along the demand curve. It also seeks to explain the factors which can shift the demand curve and why they cause the demand curve to shift.
Basically, a demand curve is a curve that shows that the number of units the market will buy in a given period at different prices that might be charged (Kotler &Armstrong, 2004). This curve is downward sloping graph and change in the demand curve can be in the form of movement along the demand curve and shift in the demand curve. Price variable is the main factor that determines the demand of a particular good or service (Benassy, 1988). Thus, the law of demand states that the higher the price, the lower the demand of the goods. This means that few people will buy products that have a high price and more people will be willing to buy products if the price is low. As a result, when price changes, there will be movement along the demand curve as illustrated in Figure 1 below.
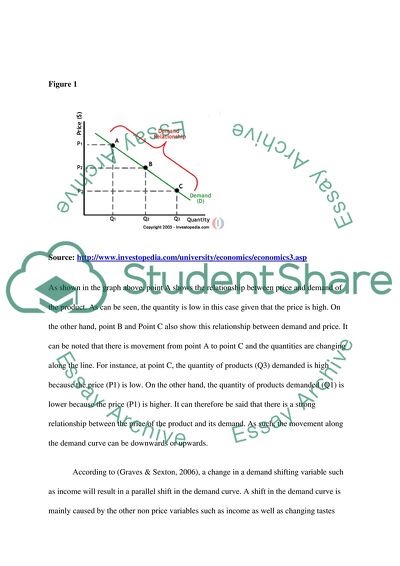
Figure 1
Source: http://www.investopedia.com/university/economics/economics3.asp
As shown in the graph above, point A shows the relationship between price and demand of the product. As can be seen, the quantity is low in this case given that the price is high. On the other hand, point B and Point C also show this relationship between demand and price. It can be noted that there is movement from point A to point C and the quantities are changing along the line. For instance, at point C, the quantity of products (Q3) demanded is high because the price (P1) is low. On the other hand, the quantity of products demanded (Q1) is lower because the price (P1) is higher. It can therefore be said that there is a strong relationship between the price of the product and its demand. As such, the movement along the demand curve can be downwards or upwards.
According to (Graves & Sexton, 2006), a change in a demand shifting variable such as income will result in a parallel shift in the demand curve. A shift in the demand curve is mainly caused by the other non price variables such as income as well as changing tastes among the consumers. This means that the demand of a particular product can shift even if the price remains the same. For instance, if the income for consumers who buy food from fast food restaurants increase, there will also likely to be a shift in demand given that the majority of them will now be able to afford the food offered. In this case, the demand curve will shift to the right which shows that there has been an increase in demand even though the price remains the same. If their income decreases, then the demand curve will shift to the right. Changing consumer tastes can also cause a shift in the demand curve. For instance, regardless of the price, the demand of smart phones is growing considerably during the current period given that the customers seek to derive valuable benefits from the products offered. Smart phones have multimedia functions that are desired by the customers. The demand curve shifts to the right. Figure 2 below illustrates the shift in the demand curve for beer.
Figure 2
Source: http://www.investopedia.com/university/economics/economics3.asp
In this graph, it can be seen that D2 is the new demand curve that can be caused by positive changes in the income or tastes of the consumers. The price can be the same but there will be a shift in the demand. On the other hand, if there is a negative change in these factors, the demand curve will shift to the left which will show a decline in the demand. In this case, if beer is the only alcoholic beverage offered in the market, then the demand curve will shift to the right as shown in the diagram above.
From the discussion above, it can be noted that the main difference between movement along the demand curve and shift in the demand curve is that movement is only influenced by price of the product while a shift in the demand curve is caused by non pricing factors such as income as well as changing tastes of the employees. On the other hand, movement along the demand curve can be an upward or downward trend along the demand curve showing the relationship between demand and price of the product. As stated by the law of demand, the higher the price of the product, the lower the demand of that product.
Another major difference is that the demand curve shifts either to the right if the demand for a particular product increases or to the left if the demand decreases. Thus, the major difference between movement along the demand curve and shift in the demand curve is that when there has been a shift in demand, the position of the curve changes either to the left or right while the position of the demand curve remains stable if there is movement along the demand curve.
The main factors as noted which can shift the demand curve to the right or left are not related to price variables. If there has been an improvement on the product such that people can derive more benefits from using it, the demand will shift to the right which shows that there has been an increase in the number of buyers willing to purchase the product regardless of its price. If the customers’ income increases, there will be likely chances of an increase in the demand of a particular product. On the other hand, if the income decreases such as the case of the global economic recession, the customers’ buying power will also decrease and this will shift the demand curve to the left.
The price may remain the same but the demand will shift. Changing consumer tastes can also cause a shift in the demand curve for a particular product. If the tastes of the consumers towards a certain product are positive, there is likely to be a positive shift in the demand curve. Essentially, consumers buy products to satisfy their needs and wants and if they are assured that they can benefit from using a particular product, they will develop a positive attitude towards it regardless of the price. This will then lead to a shift in the demand curve of that particular product. The customers can also shift their demand if they are in a position to identify the advantages of consuming a particular product.
Over and above, it can be noted that business is essentially meant to satisfy the needs and wants of the consumers. The people demand products with benefits that add up to the most value and satisfaction and it can also be noted that the law of demand goes hand in hand with price of the product. The relationship between price and demand of the product can be graphically represented using a demand curve as illustrated above. There are mainly two changes that can happen to this demand curve and these are movement along the demand curve and a shift in the demand curve. These are mainly influenced by different variables as discussed above.
The main difference between these changes is that movement along the demand curve is mainly influenced by price variables and the movement can be either up or down the curve. On the other hand, shift in the demand curve is caused by non price variable factors such as changing consumer tastes as well as changes in the consumers’ income. A shift in the demand curve means that the curve will either shift to the right or the left. If the curve shifts to the right, this will mean that there has been an increase in the demand of a particular product and if the demand curve shifts to the left, there will be a decrease in the demand of that product.
References
Benassy, JP 1988, ‘The Objective Demand Curve in General Equilibrium with Price
Makers,’ The Economic Journal, Vol. 98, No. 390, Supplement: Conference Papers. (1988), pp. 37-49, viewed 30 March, 2011,
Economics basics: Demand and supply, 2011, viewed 30 March, 2011,
Graves, PE & Sexton RL 2006, ‘Demand and supply curves: rotations versus shifts,’ Atlantic
Economic Journal, September, 2006, viewed 30 March, 2011, http://www.entrepreneur.com/tradejournals/article/167934477.html
Kotler, P & Armstrong G 2004, Principles of Marketing, Pearson Education
International, NJ.
Survey Results: Demand Schedule, ND, viewed 30 March, 2011,
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand
Importance of Derived Demand in B2B Marketing
This mostly occurs in cases where the consumer has bought the product with the main purpose being to use it for purposes of production (Bruhn, 2003).... t has to be understood that the difference between a consumer market and business to business is not the kind of products but how the products themselves are exchanged between them and the relationship that exists between the two (Dwiyyer and Tanner, 2008).... The essay "Importance of Derived demand in B2B Marketing" focuses on the critical analysis of the marketing strategies that help an organization to concentrate on the greatest opportunities to increase their earnings and attain a sustainable competitive advantage....
11 Pages
(2750 words)
Essay
Introductive Issues to Economics
Thus, before setting the price, the marketer must understand The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand.... It can therefore be said that there is a strong relationship between the price of the product and its demand.... s shown in the graph above, point A shows the relationship between price and demand for the product.... The law of demand goes hand in hand with the price of the product.... On the other hand, Point B and Point C also show this relationship between demand and price....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Essay
Relationship between Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost
Therefore, cross-price elasticity of demand is a measure of the relationship between percentage changes in the demand of one product with the percentage change in the price of others.... If both goods are substitutes then the elasticity will be positive as the increase in price in one product will make the people buy the other on and thus its demand will increase.... If the products are complements, then the elasticity will be negative as the increase in the price of one good will make the users/consumers shift to another product and it will make them leave the use of that product to avoid the extra cost....
12 Pages
(3000 words)
Term Paper
Operations Performance Objectives and Supply Chain Relationships
An example of effective packaging for food items is 'combined transit and point-of-sale packaging' which saves labour time through faster shelf loading and easy access to product and uses lesser resources.... HCF receives ingredients from its suppliers, transforms the inputs into products, and makes the supply chain moving until the product reaches the retailers (the supermarkets) and end-users.... For some fast-moving commodity like chilled foods, the cost of distribution and retail selling affect the total product cost which represents about 50 per cent of the product price (Coles 2003)....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Case Study
The Relationship between Customer Value and a Companys Distinctive Capabilities
From the paper "the relationship between Customer Value and a Companys Distinctive Capabilities" it is clear that generally speaking, the effectiveness of a business unit sales force can be evaluated indirectly by the income obtained after sales promotion.... uestion 1: the relationship between customer value and a company's distinctive capabilitiesCustomer value refers to the value derived from a product or a service by a customer.... Marketing refers to the process of informing customers of the value of the product or services....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Essay
Price Elasticity of Demand
When the calculations yield a zero measure, then there is no relationship between the products (Wetzstein 2013).... High price elasticity means that the demand for the product is extremely sensitive to changes in commodity price.... The paper "Price Elasticity of demand" highlights that a negative coefficient on the other hand shows that the items may be inferior.... Elasticity is the degree of responsiveness in supply and demand within a market in relation to price changes....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Essay
The Relationship of Internal Governance and Consumer Demand
It should be said that consumers are one of the most prominent microeconomic issues concerning businesses with product and service offerings.... The author concludes that businesses are gaining more control over consumer demand through practical marketing efforts and making proactive adjustments to internal production models and staffing objectives for better and more quality support of their business concept .... The ability to influence demand and pilot new supply strategies based on known consumer price sensitivity is a new method that considers microeconomic factors first and foremost Marketing becomes a micro level concern involving job roles, product variety, and balancing inventories....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Term Paper
Relationship between Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost
Whereas total cost refers to the sum of all the expenses incurred by a company, to produce all the units of the product.... The paper "relationship between Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost" is a great example of macro & microeconomics coursework.... The paper "relationship between Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost" is a great example of macro & microeconomics coursework.... In the said exercise basic economic concepts of marginal cost, marginal revenue, elasticity of demand, price elasticity of demand, cross price elasticity, income elasticity, profit maximization, profit, elasticity....
12 Pages
(3000 words)
Coursework
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the assignment on your topic
"The Relationship between the Product and Its Demand"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY