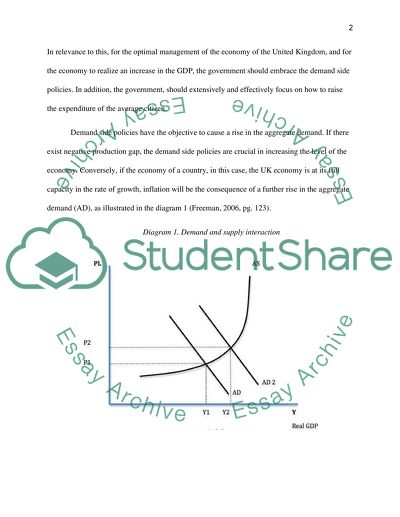
Cite this document
(“Is it necessary to use both demand and supple side policies to manage Coursework”, n.d.)
Is it necessary to use both demand and supple side policies to manage Coursework. Retrieved from https://studentshare.org/macro-microeconomics/1693002-is-it-necessary-to-use-both-demand-and-supple-side-policies-to-manage-the-uk-economy
Is it necessary to use both demand and supple side policies to manage Coursework. Retrieved from https://studentshare.org/macro-microeconomics/1693002-is-it-necessary-to-use-both-demand-and-supple-side-policies-to-manage-the-uk-economy
(Is It Necessary to Use Both Demand and Supple Side Policies to Manage Coursework)
Is It Necessary to Use Both Demand and Supple Side Policies to Manage Coursework. https://studentshare.org/macro-microeconomics/1693002-is-it-necessary-to-use-both-demand-and-supple-side-policies-to-manage-the-uk-economy.
Is It Necessary to Use Both Demand and Supple Side Policies to Manage Coursework. https://studentshare.org/macro-microeconomics/1693002-is-it-necessary-to-use-both-demand-and-supple-side-policies-to-manage-the-uk-economy.
“Is It Necessary to Use Both Demand and Supple Side Policies to Manage Coursework”, n.d. https://studentshare.org/macro-microeconomics/1693002-is-it-necessary-to-use-both-demand-and-supple-side-policies-to-manage-the-uk-economy.