StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Health Sciences & Medicine
- Way of Identifying Genes that Have Developed Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Molecular Cancer
Free
Way of Identifying Genes that Have Developed Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Molecular Cancer - Assignment Example
Summary
"Way of Identifying Genes that Have Developed Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Molecular Cancer" paper examines two approaches that are used to identify genes that have roles in drug resistance including microarray and next-generation RNA sequences. …
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER94% of users find it useful
- Subject: Health Sciences & Medicine
- Type: Assignment
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 10 (2500 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: dratke
Extract of sample "Way of Identifying Genes that Have Developed Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Molecular Cancer"
Plan study questions MED6041: The study of these articles aims to provide a framework for understanding a common way of identifying genes that have developed resistance to targeted therapies in molecular cancer.
Question 1:
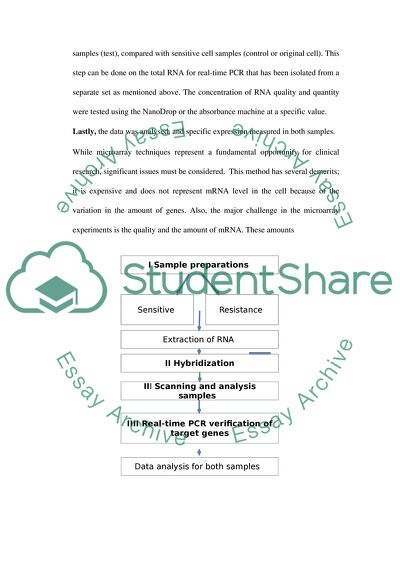
In this section, two approaches that are used to identify genes have roles in drugs resistance including microarray and next generation RNA sequences. These approaches are used to identify differential gene expression in resistance tumors cell samples (test), compared with sensitive cell samples (control or original cell)
1. Microarray:
As seen in (Figure 1) the first step is isolation from both (sensitive and resistance) samples by using buffer and RNA extraction kit (Invitrogen) to obtain mixture from cell/tissue samples provided (Bao et.al , 2014).
After RNA extraction, Microarray Hybridization is used. This technique is performed by using gene expression microarray, generate a purification and fluorescent-labeled cRNA in vitro transcription.
Scanning and analysis samples of cDNA are used to identify the differentially expressed genes. A high-resolution microarray scanner is used to visualise the hybridized microarrays. The resulting image is then analyzed using a computer and statistical software for data analysis.
The Real-time PCR verification of samples is subsequent to the analysis and verification. The microarray result determined in this experiment indicates that the expression of the human gene in the cells includes the resistant tumors cell samples (test), compared with sensitive cell samples (control or original cell). This step can be done on the total RNA for real-time PCR that has been isolated from a separate set as mentioned above. The concentration of RNA quality and quantity were tested using the NanoDrop or the absorbance machine at a specific value.
Lastly, the data was analysed, and specific expression measured in both samples.
While microarray techniques represent a fundamental opportunity for clinical research, significant issues must be considered. This method has several demerits; it is expensive and does not represent mRNA level in the cell because of the variation in the amount of genes. Also, the major challenge in the microarray experiments is the quality and the amount of mRNA. These amounts
Figure 1: Represents the workflow for analysis showing sample preparations (Step 1), hybridization (Step 2), screening samples (Step 3), data analysis and identification (Steps 4).
2. Next generation RNA sequences:
Traditional approaches sequences are wildly used as guide therapy to treat patients with cancer. This protocol is suitable because it does not require a sequenced genome, therefore allowing identification of novel transcripts. Furthermore, unlike microarray hybridization based detection, Next generation RNA sequences method has a wide range to detect genome analysis of transcription at single nucleotide resolution such alternative splicing events identification and post-transcriptional RNA editing events.
Just as any other experiment, a well-designed RNA-seq method consists of three main steps including proper replication, randomization and blocking. First, the prepared samples (test – control) is the total RNA. In general, total RNA is isolated and converted into cDNA because short RNAs, mRNAs fragmentation are typically smaller pieces that enable sequencing. Then, random hexamers or oligo (dT) primers are used to reverse transcribe for the first and second strand cDNA. The end of the 5’ and/or 3’ ends of cDNA are repaired and adapters allow hybridization of sequences, which are then correctly ligated to cDNA fragments and are amplified by PCR to add any remaining sequencing primer sequences. Lastly, these sequence data are then subjected to statistical and bioinformatics software and analysis of the differential expression is analysed, novel transcripts are identified and analysis of pathway. (See Figure 2).
While offering the major advantage of removing confounding factors, multiplexed, translocation, insertions and also for re-sequencing on an additional lane(s), without introducing sample-specific biases from samples cells. Including the ability to fully sequence large numbers of genes in a single test. However, in the next generation an RNA sequence has several limitations such as cost, time consuming process, and computational complexity.
Figure 2: Overview of analysis workflow for next generation RNA-seq transcriptional profiling.
Proteomics Approach is an additional technique that can be used. It analyzes the proteome and is used to identify and quantify the various proteins, protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions. This approaches recently has been advanced over many traditional techniques that cannot screen a large number of proteins (mentioned above). So, proteomics protocol helps to identify and validate drug targets, design and discover disease biomarkers (Jhanker et.al , 2012).
Question 2:
First section: The Experimental RNA interference (RNAi) has become a vital tool in functional genomics research. It is done through synthesis selective knockdown of gene function including double stranded RNA (dsRNA) or short interfering RNA (siRNA).
Second sections: all processes of apoptosis are controlled via several regulators known as assay discovery, which is used in-vivo and in vitro. All of these assays have advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, to test this hypothesis, an overexpression of the cDNA gene profiling to cause changes in tumour cells in the experiment. The main test that is would confirm the induction of apoptosis.
1- Annexin V/ propidium iodide (PI) assay:
This protocol is a commonly used approach in the early detection of apoptosis in a cell. The advantage of this assay is that it is more sensitive and less time consuming. Generally, the experiment involves three main steps. First, apoptotic cells were prepared by specific procedures for corresponding primary cell isolations and incubated with annexin-V protein. Secondly, the propidium iodide was added to the prepared mixture that was used to distinguish between apoptotic cells and necrotic cells. The final step is made a fluorochrome probe in a flow cytometer to realize the apoptotic cells. The estimated result will give an annexin-V-positive/PI-negative to apoptotic bodies; while necrotic cells are especially positive to annexin-V/ PI.
2- Caspase 3 Activity Assay:
This assay can be used for the quantification of activated caspase of human cells to generate apoptotic morphology. In addition, caspase 3 is a protein based on constructing a specific substrate (fluorescence signal) that is determined fluorometricaly. Moreover, it is one of the critical enzymes of apoptosis. In summary, the experiment method starts with samples are cultured in microplates and apoptosis is induced, causing an activation of caspases. Then, the caspase substrates are prediluted in an incubation buffer that is linked to a fluorescent probe, to induce proteolytic cleavage of the substrate. Finally, flow cytometry machine will detect the fluorescence signal from the sample and it would be proportional to the concentration of activated caspase 3. Assuming that our experimental samples involve apoptotic cells, we would expect to get a rise in the concentration of activated caspase 3 in the cells.
1- Terminal dUTP Nick End-labelling (TUNEL) assay:
During the late stages of apoptosis, TUNEL assay has been designed to detect apoptotic cells that undergo extensive DNA degradation. This process is founded on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) labels DNA strand breaks by catalyzing the polymerization of labeled nucleotides to free 3’-OH DNA ends. The experiment protocol is divided into specific steps. First, cell samples are fixed with formaldehyde to allow penetration of the TUNEL reaction reagents. Then, the 3 ends of fragmented DNA are incubated and incorporated with biotinylated- dUTP. Finally, flow cytometry is used to detect fluorescence signal that caused by fluorochrome reaction.
2- Nuclear morphology:
Morphological changes play a major role in the processes of apoptosis. To examine this in greater detail, sample cells were cultured and subsequently prepared for immunocytochemical characterization, then fixed with ethanol for 15 minutes at room temperature to analyse cell nuclear morphology.
3- DNA-fragmentation-based assays:
Detection of DNA fragmentation is currently one of the most frequently used techniques for highlighting apoptotic cells in tissues and is among the most reliable and characteristic hallmark of apoptosis. They all follow the same procedure as other assays (mentioned above). It is highly specific based on the high sensitivity of DNA in the apoptotic cell to thermal denaturation. ApoSTAIN is used to stain the cells samples before heat treatment and loading buffer known as formamide that denatures and is detectable by only apoptotic cells.
Advantage
Disadvantage
Annexin V (PI)
Expensive
Caspase 3 activity
(TUNEL) assay
Sensitive
High reproducibility, with good precision
Fast
- Necrotic cells can generate false positives.
-
Nuclear morphology
- We can’t get off from the stander effect 100% just only 70%.
DNA-fragmentation
Simple, accurate and fast assay for the measurement total cell number.
Specific that not detect necrotic cells or non-apoptotic
Table 1 shows the advantage and disadvantage of apoptotic tests
Question 3:
There are two approaches that are applied in studying proteins identification that interacts with the putative apoptotic portions.
1- Tandem affinity purification (TAP) mass spectrometry:
TAP is a purification technique used to identify protein-protein interactions from a cellular mixture. This protocol is based on the synthesis of TAP-tag to the target protein and its subsequent outline into a host cell. Affinity purification techniques are used to study the fusion protein and analysed by mass spectrometry. Figure (2) shows the structure of The TAP-tag.
Figure 3: Illustrates TAP-tag schematic representation of C- and N-terminal fusion constructs. It is prepared from proteins: calmodulin binding peptide (CBP), protein A (ProtA), and Tobacco Etch virus protease (TEV). (Reproduced from Xu et al., 2010)
The experiment strategy includes two main steps: first, TAP purification involves a fusion of the target protein to a TAP-tag in the host cell. Secondly, mass spectrometry was used to analyse the fused protein that was recovered by the purification techniques. Briefly, as seen in Figure 4, the fusing TAP tags are expressed in a specific expression vector usually a plasmid and presented to the tumour cells. Then, PCR method is used to integrate the N- and C-terminal TAP-tag cassettes into the genome. The protein complexes that contain the TAP-tagged protein are translated into the host cell. This allows detection the proteins of interest.
Figure 4:
The major advantage of this approach is that it analyses a wide mass range of fragmentated samples. This method is also highly sensitive and specific as a result of tandem affinity thus giving less false positives and negatives. It allows for detection of the protein complex that is formed in vivo. Disadvantages include the inability to detect any other proteins that already exist in the database.
2- Yeast Two Hybrid (Y2H):
It is consider one of the powerful molecular methods for detecting proteins: protein interacts (PPIs) with specific protein by testing the interaction between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule. This technique relies on two transcription factors including, the DNA-binding domain (DB), usually responsible for DNA binding and activating domain (AD) which is a protein that is responsible for the activation of transcription. Furthermore, candidate prey proteins are expressed in fusion with AD, while bait proteins are fused with DB. So, these proteins are expressed in the yeast host cell with reporter plasmid. After the interaction of the proteins, hybridization of the transcription factors occurs, which leads to increase in the expression of the reporter gene. The advantage of this technique is the capabiliy of disclosing multi component interactions, is sensitive and simple procured.
The methodology of this protocol is applicable in various steps throughout the process of drug discovery. It is divided into two main parts; Figure 5. First, plasmid encodes apoptotic protein which is expressed as fusion to a DNA binding domain (DBD) commonly termed the “bait”, while the second plasmid protein is expressed as a fusion to an activation domain (AD) and is known the “prey”. Then these two proteins are transferred yeast cells for co-expression. Lastly for large-scale screenings, two main method are used, (1) the library screening approach indicate multiple baits are screened against a library, and (2) the matrix approach, that illustrate specific array of defined preys that substituted for the library (Auerbach and Stagljar, 2012)
Question 4:
Molecular medical studies have played an active role in the development of the drugs for cancer treatment. So, oncologists reflected on the fact that approximately one half of the chemotherapeutic drugs are used for treatment. This part discusses how drugs discovery, design and target development of a known enzyme by utilized numerous strategies and techniques.
It is clear that enzymes are made up of amino acids that are linked together and the active site, is where the reaction is catalysed (as seen in Figure 5). This site of an enzyme shows the biological molecule reaction fits to initiate a biochemical reaction. Therefore, in the structure-guided drug design, studies prove the important function of the active site of enzyme target link with particular diseases such cancer to design or create synthetic compounds (a molecule) that fight the progression of the disease. Also, designing new drugs that target enzymes is commonly aimed to interact with the active site of the enzyme.
Normal Activity of Enzyme The Goal of Drug Design
Figure 5:
Rational design is applied to the discovery of novel lead drugs. There are two main types of drug design:
1- Ligand-based (or indirect):
The target protein structure is not required in this type. This type relies on the other molecules that bind to the biological target of interest; the minimum is only one ligand molecule.
Computer Aided Drug Design (in silico):
This methodology uses computational chemistry to determine, improve, or study drugs and relates to molecules that are biologically active. The most important goal of this methodology is to calculate the binding affinity of a given molecule to a target and the related binding kinetics.
2- Structure-based (or direct):
It is an approach where the structural proteins of the drug target are used for the development of inhibitors. This method is commonly obtained by X-ray crystallography and nano magnetic resonance (NMR) to focus on the three-dimensional structure of the active site of the target enzyme.
X-ray crystallography:
Crystallography, or the study of crystals, is the scientific discipline that is at the centre of structure-based drug design. X-ray crystallography protocol studies how substrate binds to the active site area of the target protein. This information is used to design drugs that would be predicted to bind with high affinity and specificity for computational methods.
3-De novo drug design:
De novo drug design States the art structure-based of drug design. It is divided into three main parts, structure based, in vitro assay and in vivo assay based. The structure contains individual functional groups known as “fragment” which the program chooses from a predefined library. The work done by Hartenfeller and Schneider (2011) indicates that the protocol starts with growing one preferred fragment and new building blocks are added to assemble the final ligand. Then, the target-binding pocket is saturated with preferred building blocks, which are then linked using appropriate linker fragment. This method has some limitation including costs, time-inefficiency, flexible parts are poorly resolved and the orientation of Asn, Gln and His side chains are difficult to determine (Hartenfeller and Schneider, 2011).
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Way of Identifying Genes that Have Developed Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Molecular Cancer
The Increasing Incidence of Cancer in Human Beings
cancer
... cancer is a disease wherein the body's own cells undergo uncontrolled multiplication and growth that leads to very unhealthy states leading to death.... cancer cells possess four characteristic properties which distinguish them from normal cells which are uncontrolled proliferation (growth), altered differentiation and loss of function, invasiveness and metastasis.... Based on the information available currently, it is important to find out how cancer stem cells can be identified....
21 Pages
(5250 words)
Essay
New Approach in Cancer Treatment
Cancer stem cells portray resistance to anti-cancer drugs available in the market today (Majumder, 2009:13).... Name Institution Course Instructor Date Is the New Approach in cancer Treatment Targeting cancer Stem Cells Viable?... cancer is amongst the leading non-communicable diseases causing menace in society today as it has no cure.... Much of what scientists know about cancer surrounds the fact that cancer cells have a hyperactive division rate and proliferate to large numbers in a short period....
12 Pages
(3000 words)
Essay
Candidate Cancer Meiosis Genes
Moreover, the cells in a tumor are a complex and diverse mix of cells that have different characteristics.... Research has shown that some of these genes that are only expressed in the testes are also expressed in other somatic cells when they become cancerous tumor cells.... Research has shown that some of these genes that are only expressed in the testes are also expressed in other somatic cells when they become cancerous tumor cells.... The number of CTA genes that can be used for diagnosis is less because many of these genes are also expressed in a few normal somatic cells....
24 Pages
(6000 words)
Literature review
Evaluation of Luprolide as ADT
Introduction In spite of all the dramatic advances in the understanding of disease processes, medical science, and medical technologies, cancer remains a disease of special focus in present times, because of the challenges that it continues to pose as a life-threatening disease.... Most cancer diseases tend to be chronic, with a strong possibility of causing the death of the individual, yet take years to develop, before presenting any signs and symptoms of the disease....
18 Pages
(4500 words)
Thesis
The Uses of Biotechnology in the Field of Medicine
With the parallel development of cancer cell research, hyperproliferative cancer cells were seen as a better means of vaccine production.... Secondly, cell culture-based production is more cost-efficient than egg-based production because cancer cells are much easier to culture than embryonated eggs.... Similar to egg-based production, infective virus units are inoculated into a culture of a particular cancer cell line, usually Madin Darby canine kidney (MDCK) (Szretter et al....
12 Pages
(3000 words)
Essay
E Coli and Its Colonization of Urothelial Cells
From the paper "E Coli and Its Colonization of Urothelial Cells" it is clear that photosensitizers that are positively charged at the physiological pH have been found to have optimal cytocidal activity against a broad range of bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.... Individuals with acute cystitis may also have non-obstructive pyelonephritis.... Complicated urinary tract infections occur in individuals who have abnormalities in the genitourinary tract....
22 Pages
(5500 words)
Literature review
Cancer Chemotherapy
cancer eventually affects everyone's life in some respect.... Each year, approximately 70,000 people die from cancer in Canada, and the numbers are progressively increasing.... (Budwig) An uncontrollable growth of cells is the main distinguishing characteristic of cancer.... In addition to the uncontrollable growth of cells once the body is inflicted with cancer these cells grow at an explosive rate.... Even in the cases where the cancer has been detected early it is still difficult to treat and manage.
...
14 Pages
(3500 words)
Essay
Determining HER2 Expression and HER2 Glycosylation Changes
This research paper called "Determining HER2 Expression and HER2 Glycosylation Changes" outlines the amplification of the HER2/neu gene protein and the glycosylation changes connection associated with the biomarkers of breast cancer or cell lines.... This paper analyzes the amplification or expression of the HER2 in the secondary breast cancer cell line compared to the primary cell line.... The study aims would also illustrate the extra HER2 receptor stimulation of cancer cells while contrasting the validation of HER-2 protein overexpression and amplification in the secondary breast cancer lines compared to the primary cancer line (Kucab, 2009)....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Research Paper
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the assignment on your topic
"Way of Identifying Genes that Have Developed Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Molecular Cancer"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY