StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Chemistry
- Measuring the Rate of Osmosis Using
Free
Measuring the Rate of Osmosis Using - Lab Report Example
Summary
The author of the "Measuring the Rate of Osmosis Using" paper examines the phenomenon of the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane from a region in which it is highly concentrated to a region in which its concentration is lower. …
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER92.9% of users find it useful
- Subject: Chemistry
- Type: Lab Report
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: lockmanjuana
Extract of sample "Measuring the Rate of Osmosis Using"
Introduction: Osmosis A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solution. A solution is a homogeneous, liquid mixture of two or more substances.A Solvent is the dissolving agent of a solution. Water is the most versatile solvent known. This dispersal of molecules is called diffusion and is defined as the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The rate of this movement can be affected by:
1. The steepness of the concentration gradient between the two materials.
2. The molecular weight of the molecules.
3. The temperature and pressure of the substances.
Diffusion can occur across membranes if the membrane has a molecular structure to allow the molecules of the diffusing substance to pass through it. The membrane is said to be permeable to the diffusing substance. Some membranes may have a molecular structure such that certain substances can diffuse through them but other substances cannot. Such membranes are called selectively permeable membranes. The ability of a molecule to pass through a membrane is dependent on its molecular size and structure. The movement of many materials into, out of, and throughout living cells is often by simple diffusion.
A special kind of diffusion is the phenomenon known as osmosis. Simply defined in biological systems, osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane from a region in which it is highly concentrated to a region in which its concentration is lower. Since all cells contain molecules in solution (known as solutes) that cannot pass through the membrane, osmosis always occurs when cells are placed in dilute or concentrated aqueous solutions. When comparing solutions, the term “tonicity” is used. Tonicity is defined as the relative amount of solutes in a solution when compared to another solution. A solution with a higher concentration of solutes is said to be hypertonic, while a solution with a lower concentration of solutes is said to be hypotonic. If two solutions contain equal concentrations of solutes they are said to be isotonic.
Observations:
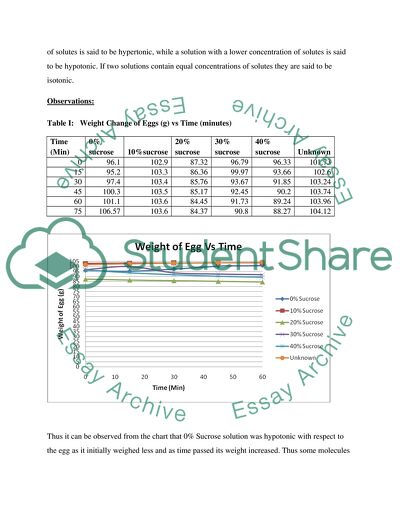
Table I: Weight Change of Eggs (g) vs Time (minutes)
Time (Min)
0% sucrose
10%sucrose
20% sucrose
30% sucrose
40% sucrose
Unknown
0
96.1
102.9
87.32
96.79
96.33
101.73
15
95.2
103.3
86.36
99.97
93.66
102.6
30
97.4
103.4
85.76
93.67
91.85
103.24
45
100.3
103.5
85.17
92.45
90.2
103.74
60
101.1
103.6
84.45
91.73
89.24
103.96
75
106.57
103.6
84.37
90.8
88.27
104.12
Thus it can be observed from the chart that 0% Sucrose solution was hypotonic with respect to the egg as it initially weighed less and as time passed its weight increased. Thus some molecules of the sucrose solution diffused into the deshelled egg membrane with relatively lesser concentration by osmosis to neutralize the concentration gradient.
On the other hand, it can be observed from the graph that the solution with 30% sucrose solution was hypertonic with respect to the egg. This is because initially the egg weighed more and as time passed its weight decreased. Thus some solute particles diffused from the egg into the surrounding 0% sucrose solution of lesser concentration by osmosis.
Table II: Weight Change of Eggs (g) vs Time (minutes)
Time (Min)
0% sucrose
10%sucrose
20% sucrose
30% sucrose
40% sucrose
Unknown
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
15
0.9
-0.4
0.96
1.82
2.67
-0.87
30
-1.3
-0.5
1.56
3.12
4.48
-1.51
45
-4.2
-0.6
2.15
4.34
6.13
-2.01
60
-5
-0.7
2.67
5.06
7.09
-2.23
75
-10.97
-0.7
2.95
5.99
8.06
-2.39
a. What conclusion can you draw from the data in this graph?
Ans a. From the graph, we can conclude that 0% sucrose solution was extremely hypotonic with respect to the egg. This is because the change in weight in the 0% solution egg is most pronounced. This indicates that there was a steeper concentration gradient between the deshelled egg inner environment and the outer sucrose solution and it took longer to come to similar concentration
The concentration gradient between the remaining sucrose solutions and the internal egg environments were less steep.
Solution with 40% sucrose was extremely hypertonic with respect to the deshelled egg. This is because its weight increased linearly at almost all time intervals. This suggests that molecules from the sucrose solution diffused into the egg by osmosis thus increasing its weight accordingly.
The solution with unknown concentration of sucrose is positioned between the 0% and 10 % sucrose concentration curves. Thus its concentration is expected to be around the same range.
b. Which solutions were hypotonic? Hypertonic? Isotonic?
Ans b:
Solution
Sucrose Concentration
Hypotonic
0%, Unknown
Hypertonic
20%, 30%, 40%
Isotonic
10%
Table III: Total Weight Change of Eggs (g) vs Sucrose Concentration (%)
Time (Min)
0% sucrose
10% sucrose
20% sucrose
30% sucrose
40% sucrose
Unknown
Total Weight Change
-10.47
-0.7
2.95
5.99
8.06
-2.39
Q. 1 Determine the isotonic point of the contents of a chicken egg.
From the graph trendline, we get the equation of the graph as:
y = 43.75x - 7.584
At the isotonic point, y i.e Total weight change will be 0. Thus substituting in the equation:
0= 43.75x - 7.584
43.75x= 7.584
X= 7.584/43.75
X= 0.1733
Thus the isotonic point is at 17.33%
Q2. Determine the concentration of the unknown solution.
From the graph trendline, we get the equation of the graph as:
y = 43.75x - 7.584
The total weight change for the Unknown concentration solution i.e the value of y= -2.39
Thus,
-2.39 = 43.75x – 7.584
43.5x= 5.194
X= 5.194/43.5
X= 0.1194
Thus Unknown concentration of sucrose solution is 11.94%
It is hence important to understand the concept of osmosis and practically demonstrate it along with analytical graphs, observations and results.
We encounter the phenomenon of osmosis quite frequently in day to day life:
Examples:
Feeling excessively thirsty in summers or in desert like dry solutions or whenever we consume too much of dry food like biscuit is the body’s response to the environment to balance for body fluids.
Salt curing of meat in brine is another example of osmosis.
In plants osmosis is at least partially responsible for the absorption of soil water by root hairs and for the elevation of the liquid to the leaves of the plant. However, plants wilt when watered with saltwater or treated with too much fertilizer, since the soil around their roots then becomes hypertonic.
Freshwater and saltwater aquarium fish placed in water of a different salinity than that they are adapted to will die quickly, and in the case of saltwater fish, dramatically.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Measuring the Rate of Osmosis Using
Studying the Impact of Solute Concentration on the Rate of Osmosis
The paper "Studying the Impact of Solute Concentration on the rate of osmosis" discusses that Osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules through a selective membrane (Freeman, 2010).... This experiment was carried out in order to determine how the rate of osmosis changes under different solute concentrations.... By studying the weights of the dialysis tubings after the experiment was over, the conclusion arrived that the rate of osmosis between two solutions separated by a selective membrane is heavily dependent on the solute concentration in the two solutions....
3 Pages
(750 words)
Lab Report
Research Proposal on the effect of hydrostatic pressure on plants
Similarly, Voet, Judith, Voet and Pratt, (56) sought to investigated the application of osmosis in Biochemistry.... Water level and pressure will be monitored every 2-3 days to insure their constancy using two method while the water flow measurements are taken.... Water level and pressure will be monitored every 2-3 days to insure their constancy using two methods.... Fundamentally, it is the minimum pressure required to nullify osmosis....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Research Proposal
Produced Water Treatment
Produced water is generated in the process of lifting oil and gas from water-bearing formations–typically sea beds.... Water is brought along with oil and gas.... ... ... they are lifted to the surface (Stewart 21).... his is very useful in places like agricultural sector, household and also drinking water when the water is treated therefore it should not be wasted....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Term Paper
Membrane Permeability and Cell Division
the rate at which these ions pass thus depends on the permeability to each particular substance, the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the substances or molecules.... Ions and other molecules pass through it by diffusion, osmosis, or facilitated diffusion.... The construct of the membrane also determines the movement rate and permeability....
10 Pages
(2500 words)
Lab Report
The Effect of Salinity on the Cytoplasm and Sap Concentrations between Potatoes, Swedes and Carrots
The aim of this experiment is to establish the effect of salt solution concentrations on osmosis potential as the main variables used to compare potato tubers, root carrots, and Swedes bulbs.... There are two factors that influence osmosis.... The experiment "The Effect of Salinity on the Cytoplasm and Sap Concentrations between Potatoes, Swedes, and Carrots" considers reduction in mass through loss of water from plant tissues placed in varying salt concentrations to investigate salt tolerance and composition of their cell sap and cytoplasm....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Lab Report
Technical Languages in Biology
For instance, the phrase, 'The energy content of food is measured by burning a sample and measuring the amount of heat energy released', explains what the experiment was about by the use of a few words.... Lexical density has been achieved by using clauses that contain content words that provide more information about the text....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Assignment
Regulation of Water and Solute Balance in Cells
One of the key processes that are involved in the exchange of these substances is the diffusion and osmosis processes.... osmosis is a special diffusion process in which molecules and ions move through a semi-permeable membrane from a solution that is less concentrated to a more concentrated solution.... These pores are small enough to enable the tubing to be used as a model to demonstrate diffusion and osmosis across the cell membrane....
9 Pages
(2250 words)
Assignment
Desalination Issue in Australia
The Reverse osmosis plant can handle a range of flow rates from a few up to 750,000 L/day.... Reverse osmosis can eliminate other chemicals in the water apart from salts.... Some of the techniques employ distillation or freezing techniques, whereas others make use of ion exchange and Electrodialysis or Reverse osmosis....
48 Pages
(12000 words)
Research Paper
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the lab report on your topic
"Measuring the Rate of Osmosis Using"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY