StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Macro & Microeconomics
- Intermediate Micro and Macro Economics
Free
Intermediate Micro and Macro Economics - Assignment Example
Summary
The IS curve explains the relationship between the interest rates and the goods and services demanded while the LM curve shows the…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER94.4% of users find it useful
- Subject: Macro & Microeconomics
- Type: Assignment
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: noelia94
Extract of sample "Intermediate Micro and Macro Economics"
INTERMEDIATE MICRO AND MACRO ECONOMICS By Location QUESTION IS-LM framework defines the relationship between the interest rates and the real output in the goods and services market and the money market. The IS curve explains the relationship between the interest rates and the goods and services demanded while the LM curve shows the relationship between the money supply and the money demanded (Mankiw,p104).
As defined by the Keynesians, liquidity trap refers to a situation where the prevailing interest rates are low and saving rates are high prompting ineffective monetary policy (Howard and Snowdon p131). In this situation consumers tend to avoid bonds and save their funds anticipating rise in the interest rates. The concept indicates that the rate of interest is determined by the supply of money (saving) and the desire to hold wealth in cash. Thus when the economy is in liquidity trap where the supply of money by central bank in private banking fails to decrease interest rates hence making the monetary policy ineffective. This happens when people hold cash because they anticipate events like deflation and insufficient aggregate demand.
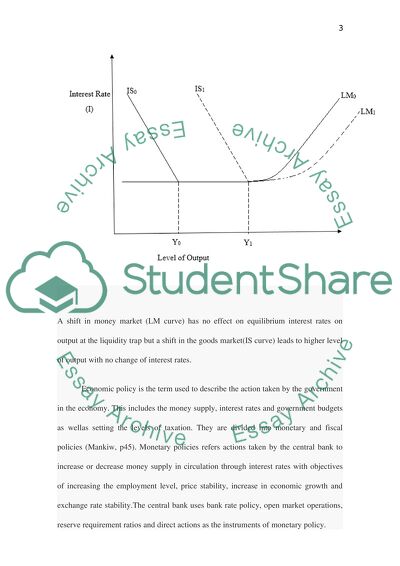
Classical Keynesian view argues that if the demand for money only reflects income and does not respond to the interest rates, the demand for money is inelastic rendering fiscal policy ineffective due to crowding out effect. On the other hand, monetary policy is effective because an increase in money supply leads to an increase in output and decreases interest rates. In the liquidity trap where interest rates are low with an anticipated rise, LM curve will be close to horizontal.
A shift in money market (LM curve) has no effect on equilibrium interest rates on output at the liquidity trap but a shift in the goods market(IS curve) leads to higher level of output with no change of interest rates.
Economic policy is the term used to describe the action taken by the government in the economy. This includes the money supply, interest rates and government budgets as wellas setting the levels of taxation. They are divided into monetary and fiscal policies (Mankiw, p45). Monetary policies refers actions taken by the central bank to increase or decrease money supply in circulation through interest rates with objectives of increasing the employment level, price stability, increase in economic growth and exchange rate stability.The central bank uses bank rate policy, open market operations, reserve requirement ratios and direct actions as the instruments of monetary policy.
Fiscal policy refers to the action by the government regarding spending, consumption and investment. Y=C+I+G.
An increase in government (G) spending will increase the goods market (IS) curve to IS1 in the diagram above. This will increase the level of output at the liquidity trap while the interest rates remains constant.
A decrease in taxation will cause the IS function to shift to right similar to the increase in the government spending while an increase will lower the level of output while the interestrates remain the same thus shifting the IS curve inwards to the left.
Wealth effect refers to a situation where individuals change their level of spending due to perceived increase in wealth. The changes in individual’s wealth causes changes in their consumption. People spend ore when their wealth increase or when they perceive themselves to be rich. When there is no wealth effect the aggregate demand does not increase because the consumer does not change his consumption habits.
The main difference in the aggregate demand when the economy is in the liquidity trap and when there is no wealth effect is that in the liquidity trap, aggregate demand will increase due to increase in the level of consumption, reduced taxation and increased government spending but when there is no wealth effect the demand will remain the same when either wealth increases or decreases as the cheap items can be purchased at all times.
QUESTION 2
The DAD-DAS framework was advanced to analyse the fluctuations in the business cycle and their effects on the monetary policy of the government (Mankiw, p115 and Howard and Snowdon p140). DAD-DAS with expectations allows the inclusion of flexible forms of inflation expectations to be determined as weighted average of the past inflation rate and inflation target thus bringing this treatment closer to rational expectations where disinflation is costless given a credible inflation target. The Dynamic aggregate Demand and aggregate supply model main goal is to understand the correlation between the inflationand output that willlead to equilibrium, economic fluctuations and business cycles.
The demand side of this model is illustrated with an IS equationYt = Ῡt – α (rt – ρ) + ϵt where t is the output gap which is the difference in percentage between the actual output and the natural rate of output. in the model refers to the natural real interest rate in the long-run and represents an elasticity parameter, Yt represents the total output, Ῡt refers to the natural level of output of the economy,
The output gap affects the current inflation since higher output increases the marginal cost of production. The adaptive expectations entails capturing the future inflation rate as mixture of the current inflation while the rational adaptations assume the future inflation target of the central bank if the target is credible. Increasing the level of production permanently by the government the growth should be reflected in Ῡt. The increase in output increases consumption because people are richer and thus spend more.
Rational expectations requires the expectations of the short- run and long-run to be studied in the model jointly. It links changes in savings in the monetary sector with each movement resulting in new decisions and expectations thus changing the formulation of the model by adding different variables to the formulas giving the economic model additional power to observe and learn fluctuations in the economy and the implemented policy effects.
Equilibrium occurs at the point where DAD and DAS intersects. In the short-run, the increase in the aggregate demand makes the DAD to shift to the right prompting an increase in the price of the commodity thus increasing inflation. In the long-run, as the national output increases, the supply increases and hence the aggregate demand also increases. Using the graph above, the increase in national output from Y1 to Y2 increases the DAD1 to DAD2 this causes the DAS to shift from DAS1 to DAS 2 and thus shift the equilibrium from A to B with no change in inflation.
A permanent increase in the county’s output prompts an outward shift of the long run aggregate supply through increase in the supply of production factors to increase productivity and adopting the latest technology. This shift is similar to a shift in the production possibility frontier.
π refers to the inflation rate.
QUESTION 3
Determining the equilibrium expression
Given the equations on the functioning of the economy, the equilibrium equation can be determined using the following steps:
Y = C + I + G
C = C0 + c (Y + TR - T0 - t Y)
I = I0
G = G0
Where TR refers to transfer payments
T= T0+ t Y
step i. substituting the equations for three aggregate expenditure components gives the following
Y = C0 + c (Y + TR - T0 - t • Y) + I0 + G0
Step ii. Applying the equilibrium principal where annual expenditure equals total output
Y = C
Step iii. Substituting C from the first step into the equilibrium state in Step 2:
Y = C0 + c (Y + TR - T0 - t • Y) + I0 + G0
Step iv. Putting the like Y terms together on the left hand side to solve for Y gives;
Y - c Y + c* t Y = c TR - c T0 + C0 + I0 + G0
Y(1 - c + c • t ) = c TR - c T0 + C0 + I0 + G0
Y[1 - c • (1 - t )] = c TR - c T0 + C0 + I0 + G0
Y = 1 (c TR - c T0 + C0 + I0 + G0)
1 - c (1 - t )
Y= c TR - c T0 + C0 + I0 + G0
1 - c (1 - t )
From the above, c is the marginal propensity to consume out of disposable income whereas c (1-t) is the MPC out of national income. a student in order to help you with your studies. This is not an example of the work written by our professional essay w
Autonomous consumption is the consumption that is independent on the level of income and thus can be through savings and borrowing. If the autonomous consumption increases, it leads to dissaving which consequentially decreases the investment with a net effect of decreasing the equilibrium output. Savings and investment are directly related, increasing autonomous consumption decreases the amount of savings which are available for investment. Using the equilibrium expression derived above, the decrease in investment will result to a decrease in the equilibrium income.
Bibliography
Howard, R and Snowdon, B, 2005, Modern macroeconomics. 3rd ed. United Kingdom: Edward Elgar Publishing, Inc.
Mankiw, N.G, 2010, Macroeconomics. 7th Ed. New York: Worth publishers.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Intermediate Micro and Macro Economics
The Contemporary Global Economy
This admission essay "The Contemporary Global Economy" discusses the macro-economic performance of the UK in terms of the balance of payments.... On the other hand, Brazil re-initiated its macro-economic policymaking organizations in the late 1990s.... his and such other reforms had been done to stabilize the macro-economic department of Brazil and also to enhance the abilities of the policymakers to encounter adverse situations.... The main purpose of this in-depth paper is to investigate and present the findings of the AMR regarding the macro-economic structure of the United Kingdom and to compare it with that of Brazil's (Altman, 2011)....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Admission/Application Essay
Mathematics as a Discipline Has a Very Important Place
Which of these two parts share proximity with economics theory The undergraduate economics prerequisite should be specifically for differential or integral or for both In the following paragraphs I intend to address this question of the significance of calculus learning for the intermediate students learning micro and macroeconomic theory by replicating the article, "Does more calculus improve student learning in intermediate micro and macroeconomic theory", Co-authored by J....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Essay
Economic Consequences of Credit Market Failure in Uganda
It is in this way that micro-finance builds a bridge between micro-economic opportunities for individuals and macro-economic performance of the economy.... In an impoverished country, albeit one experiencing rapid economic growth, opportunities of individuals and therefore indeed opportunities for macro-economic growth are likely to be constrained by lack of access to resources to invest....
9 Pages
(2250 words)
Term Paper
Social Capital and Political Fantasy
Werner presented an article about systematic competitiveness done by the scientists of a German Development Institute explaining that industrial competitiveness does not result from a stable macro-economic framework or of entrepreneurship in the micro-level.... It was clearly shown that the macro-level has to secure stable conditions that guarantee the functioning of the market.... The trade policy under this macro-level was said to have promoted active integration either by general or selective liberalization of imports....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Assignment
Uganda: Economic Consequences of Credit Market Failure
"Uganda: Economic Consequences of Credit Market Failure" paper is a blueprint for the consequences of the failure of credit market failure on the growth of the Ugandan Economy.... It contains recommendations for the stabilization of the Ugandan credit market according to the Economic set-up of Uganda....
8 Pages
(2000 words)
Case Study
Macro Levels of Language Policy and Planning
In the research essay 'macro Levels of Language Policy and Planning' the author discusses four main aspects of macro (large-scale) language planning: these are status planning, corpus planning, acquisition planning and more recently, prestige planning.... here are four main aspects of macro (large-scale) language planning and these are status planning, corpus planning, acquisition planning and more recently, prestige planning.... This new critical approach to language studies realizes planning can occur at several levels at once and these are the macro and the micro level....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Assignment
Global Macroeconomic Imbalances as the Cause of the Crisis
The paper 'Global Macroeconomic Imbalances as the Cause of the Crisis ' is an exciting example of a macro & microeconomics essay.... The paper 'Global Macroeconomic Imbalances as the Cause of the Crisis ' is an exciting example of a macro & microeconomics essay.... It is argued that macro-economic policies could have been adopted by nations in order to reduce the global imbalances; however, they were not considered to be sufficient to prevent the crisis from occurring....
13 Pages
(3250 words)
Essay
Economics and the Legal Environment
It is advisable to go through the different micro and macroeconomic factors that may affect the business.... The coursework "economics and the Legal Environment" challenges faced ABC Kitchens on a daily basis.... This paper outlines macro- and micro-economic factors, such as savings, interest rate, economic growth, inflation, cvompetition, labor, production attitude....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Coursework
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the assignment on your topic
"Intermediate Micro and Macro Economics"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY