StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Macro & Microeconomics
- Analysis of Economic Profit
Free
Analysis of Economic Profit - Assignment Example
Summary
Therefore the Marginal Revenue generated by Minnie’s is always less (lower) than the price that Minnie is able to charge for the unit sold since each reduction in price causes unit revenue to decline on every…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER94.9% of users find it useful
- Subject: Macro & Microeconomics
- Type: Assignment
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: godfrey02
Extract of sample "Analysis of Economic Profit"
1A, Total revenue equals price multiplied by quantity sold. Marginal revenue equals the change in total revenue when the quantity sold increases by one unit.
In a monopoly the firm determines the entire industry’s sales. Therefore the Marginal Revenue generated by Minnie’s is always less (lower) than the price that Minnie is able to charge for the unit sold since each reduction in price causes unit revenue to decline on every good the firm sells.
B, A monopoly maximizes economic profit by producing the quantity at which
MR = MC.
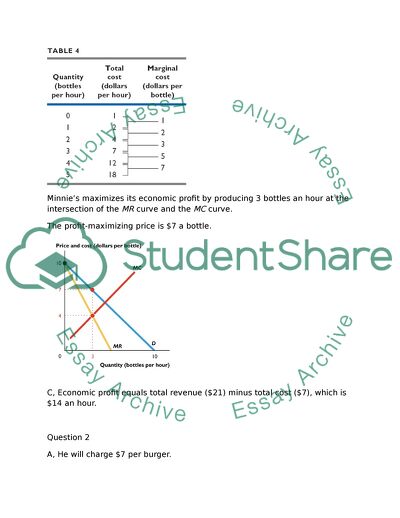
Marginal cost, MC, is the change in total cost when the quantity produced increases by 1 bottle. See table.
Minnie’s maximizes its economic profit by producing 3 bottles an hour at the intersection of the MR curve and the MC curve.
The profit-maximizing price is $7 a bottle.
C, Economic profit equals total revenue ($21) minus total cost ($7), which is $14 an hour.
Question 2
A, He will charge $7 per burger.
4 meals will be sold
Producer surplus is 28-20 = $8
Consumer surplus is 30-28 = 2
B, He will charge $7, $8 and $15.
3 meals will be sold
Producer surplus will be 30-20 = 10
Consumer surplus will be 30-30 = 0
C, If there was another restaurant in town then it would become a duopoly which would mean that if both the restaurants charge the same price for the burgers, the consumer demand will be split between them.
If there are many restaurants in town, then it would become a competitive market and the price of one restaurant would not affect the quantity demanded by the consumers.
D,
QUESTION 3
Airlines and other travel companies use differentiated pricing regularly, as they sell travel products and services simultaneously to different market segments. This is often done by assigning capacity to various booking classes, which sell for different prices and which may be linked to fare restrictions. The restrictions or "fences" help ensure that market segments buy in the booking class range that has been established for them. For example, schedule-sensitive business passengers who are willing to pay $300 for a seat from city A to city B cannot purchase a $150 ticket because the $150 booking class contains a requirement for a Saturday night stay, or a 15-day advance purchase, or another fare rule that discourages, minimizes, or effectively prevents a sale to business passengers.
Consumer surplus would be more without the price discrimination.
Consumers would pay less without price discrimination.
QUESTION 4
Product bundling is the process of securing two or more necessary goods or services from a single vendor. This strategy usually provides several advantages, including saving a great deal of money.
Companies may choose to bundle goods for several reasons, including cost efficiency, market opportunities to enhance profits, and competitive strategy. Due to economies of scale, bundling may result in cost savings on the supply side. For instance, in some scenarios a company may save on packaging and inventory costs by bundling products rather than carrying them separately. There has been a fair amount of published research delving into what kinds of bundling practices are most likely to produce cost savings. Factors a company must consider include whether the bundled products compete with each other and whether the demand for the bundled products is positively or negatively correlated.
The firms are more likely to bundle goods that are elastic as the price of the bundle goods is usually lower than the price of each individual good combined. That means that as the price goes down, the quantity demanded of the product would by a greater percentage leading to higher revenues for the firm.
QUESTION 5
The nash equilibrium in this question is 1st box which has A:$25 and B:$15.
QUESTION 6
A,
Quantity of Labor
Total Product
Marginal Product
0
0
0
1
7
7
2
13
6
3
18
5
4
22
4
5
25
3
6
26
1
B,
Quantity of Labor
Total Product
MP of Labor
Value of MP of Labor
0
0
0
0
1
7
7
70
2
13
6
60
3
18
5
50
4
22
4
40
5
25
3
30
6
26
1
10
C, The firm should hire 3 workers as at that quantity the Marginal Product of labor equals wage.
Question 7
A,
The government can respond to externalities in one of two ways
1. Command-and-control policies regulate behavior directly.
2. Market-based policies provide incentives so that private decision makers will choose to solve the problem on their own.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the government agency with the task of developing and enforcing regulations aimed at protecting the environment.
Environmental regulations can take many forms such as EPA dictates a maximum level of pollution or requires firms to adopt a particular technology to reduce emissions.
Market-Based Policy 1: Corrective Taxes and Subsidies
Taxes enacted to deal with the effects of negative externalities are called corrective taxes or Pigovian taxes. The government can internalize the externality by taxing activities that have negative externalities and subsidizing activities that have positive externalities.
Economists usually prefer corrective taxes to regulations as a way to deal with pollution because they can reduce pollution at a lower cost to society. An ideal corrective tax would equal the external cost from an activity with negative externalities. An ideal corrective subsidy would equal the external benefit from an activity with positive externalities.
B,
Education has a positive externality.
Cigarette has a negative externality.
The private benefits of education are higher salaries in the future, higher social status in the community and a better life. The public benefits of education are less dependent on social welfare, becoming a more productive citizen of the country.
The private benefit of the cigarette is enjoying a smoke, getting relaxed. The public cost of it include making more people passive smokers, higher risk of catching a disease such as cancer and becoming dependent on the state.
QUESTION 8
In economics, the tragedy of the commons is the depletion of a shared resource by individuals, acting independently and rationally according to each ones self-interest, despite their understanding that depleting the common resource is contrary to their long-term best interests.
An example from Bahrain is of the burning of fossil fuels and using up oil and contributing towards global warming.
Another example is of overfishing in the oceans leading to mass depletion in the fish population in the world.
Read
More
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the assignment on your topic
"Analysis of Economic Profit"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY