StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Design & Technology
- Software Implementation
Free
Software Implementation - Report Example
Summary
This report "Software Implementation" discusses the system that must put into consideration another requirement that is non-behavioral for example ensuring that the process of locating a free EMT should take the least time possible. The screens should be few to avoid complexity…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER98.5% of users find it useful
- Subject: Design & Technology
- Type: Report
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: kirlinkyleigh
Extract of sample "Software Implementation"
Systems analysis and design Number Part Project Management (a) Network Diagram (b) the shortest completion time is calculated by taking the shortest route that a project can be completed. This is obtaied by taking the shortest route that can be taken to complete the project.
2 weeks+3 weeks +3 weeks +7 weeks +3 weeks +4 weeks +2 weeks = 16 weeks.
(c) the critical path is the path that is highlight in red. This is the longest time that a project can take to be completed and hence need to be checked by apply crash program methods.
(d) If the duration for activity 6 is increased from one week to 6 weeks, thwe changes that will be our depend on the float time. If float time is zero, then the completion time will be increased from 16 weeks to 22 weeks. This will have affected the organisation in terms of resources due to delay. If the float time is six or more weeks then the project completion time is not affected
(e) Gantt chart for the project
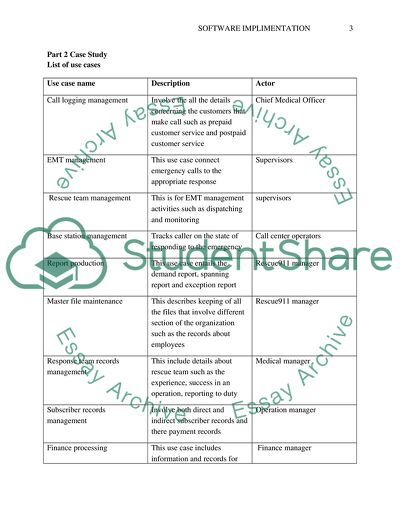
Part 2 Case Study
List of use cases
Use case name
Description
Actor
Call logging management
Involve the all the details concerning the customers that make call such as prepaid customer service and postpaid customer service
Chief Medical Officer
EMT management
This use case connect emergency calls to the appropriate response
Supervisors
Rescue team management
This is for EMT management activities such as dispatching and monitoring
supervisors
Base station management
Tracks caller on the state of responding to the emergency
Call center operators
Report production
This use case entails the demand report, spanning report and exception report
Rescue911 manager
Master file maintenance
This describes keeping of all the files that involve different section of the organization such as the records about employees
Rescue911 manager
Response team records management
This include details about rescue team such as the experience, success in an operation, reporting to duty
Medical manager
Subscriber records management
Involve both direct and indirect subscriber records and there payment records
Operation manager
Finance processing
This use case includes information and records for billing, vehicle and asset management; and accounting and finance.
Finance manager
3. Detailed description of Log Emergency Call” use case
Use case: log Emergency call
ID: UC2
Scope: The person that operates the system receives an incoming call then he/she enters the details of the incident then the appropriate emergency medical team is dispatched.
Stakeholders:
The person that made the emergency call
The medical manager who decides the suitable EMT to attend that particular case.
The core actor: The emergency center operator that is on duty
Precondition: The person operating the system must enter the user name and the password,
Trigger: The call that has been made by the victim is channeled to the operator by the system in the call center
Successful operation entails:
The call made by the client is recorded.
The EMT has been send to the scene of the incident.
The details of the incident are recorded and stored I the system
During an ideal success scenario:
The call system starts by taking down the details of the call. Then it tries to identify the physical location of the caller using the address. After that the operator notes the location of the incident. The system then checks the number of EMT that are on duty and available for dispatch at that particular time.
The system then gives the list of available EMT ant their proximity to the place where the incident is.
The operator identifies the EMT to attend to that particular case according to the experience and the severity of the case.
Then the system sends the details of the incident to the EMT that has been identified to handle that case.
Lastly the system saves all the details about the entire operation then s it terminates the recording.
Variation
If the call made is via a mobile phone, then the operator is supposed to identify the location of the caller.
For the case of a caller who makes a call for no apparent reason the system terminate the operation and lowers the priority given to that caller.
When the incident is minor that only first aid can be administered, the first aid instruction of the case is sent and the operation terminated.
When the severity of the incident is critical, then a more experienced team of EMT is dispatched.
In a situation where the the physical location of the caller cannot be identified, the system prompt the operator to reduce the priority of that case on the basis of inability to identify the location and hence the operator decide on the priority level to accord.
The all EMT teams are engaged in other cases the, the system gives the operator the reason why low priority is given to the incident.
When there is breakdown in communication between the system and the EMT team who is supposes to attend a case, the system repeats the procedure of connecting the team.
In case there is an issue with the communication in all the units, the dispatch is availed by use of mobile after the system has provided the necessary details about the incident.
The system must put in consideration other requirement that is non-behavioral for example ensuring that the process of locating a free EMT should take the least time possible. The screens that are presented to the operator should be few to avoid complexity and also the message that is passed between the EMT team and the other unit be secured using encryption methodologies to prevent eavesdrop attacker who might have malicious intention
(4) Entity relationship diagram
(5) Decision table
ID
Type
Verify Method
Risk
Status
1
Functional
Test
High
approved
2
Functional
Test
High
Approved
3
Functional
Test
Medium
Approved
4
Functional
Test
Medium
Approved
5
Functional
Test
Medium
Approved
6
Functional
Test
Low
Approved
7
Functional
Test
Medium
Approved
8
Functional
Test
Low
Approved
9
Functional
Test
Low
Approved
10
Functional
test
Low
Approved
11
performance
Demonstration
high
approved
(6) Activity Diagram.
Reference
Kendall, K., & Kendall, J. (2010). Systems Analysis and Design. Pearson Prentice Hall.
Read
More
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the report on your topic
"Software Implementation"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY