StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Macro & Microeconomics
- International Monetary Economics
Free
International Monetary Economics - Example
Summary
International Monetary Economics is a subsidiary of economics which offers a platform for evaluating money and its roles as medium of exchange, division of account and store of value over the international boundaries through international trade. This essay seeks to dissect…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER95.4% of users find it useful
- Subject: Macro & Microeconomics
- Type:
- Level: Masters
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: chelseykuhn
Extract of sample "International Monetary Economics"
International monetary economics of affiliation Introduction International Monetary Economics is a subsidiary of economics which offers a platform for evaluating money and its roles as medium of exchange, division of account and store of value over the international boundaries through international trade. This essay seeks to dissect various aspects of international monetary economics relative to the international trade dynamics. These may include partial equilibrium analysis in a single industry, costs and benefits of tariffs, export subsidies, import quotas, Gross National Product, balance of payments, exchange rates and control of money supply.
Supply, Demand, and Trade in a Single Industry
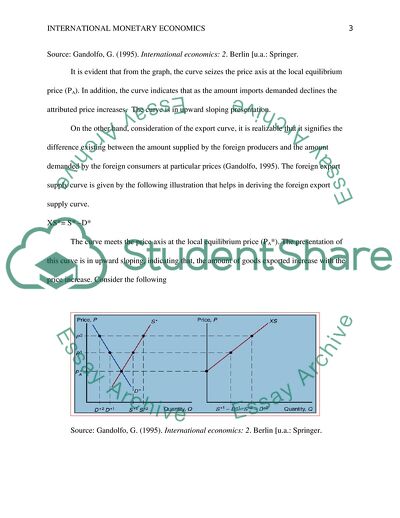
The law of supply and demand in a single industry like that of tea or wheat across different borders is occasioned by the nature of tariff that exists. A tariff refers to the tax charged on imported products (Gandolfo, 1995). The trend difference in which home consumers demand goods and the amount produced and supplied by the home producers translates to an import demand curve when particular prices are applied. Consider the following example of an import demand curve which is given by the equation
MD= D-S
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
It is evident that from the graph, the curve seizes the price axis at the local equilibrium price (PA). In addition, the curve indicates that as the amount imports demanded declines the attributed price increases. The curve is in upward sloping presentation.
On the other hand, consideration of the export curve, it is realizable that it signifies the difference existing between the amount supplied by the foreign producers and the amount demanded by the foreign consumers at particular prices (Gandolfo, 1995). The foreign export supply curve is given by the following illustration that helps in deriving the foreign export supply curve.
XS*= S* –D*
The curve meets the price axis at the local equilibrium price (PA*). The presentation of this curve is in upward sloping, indicating that, the amount of goods exported increase with the price increase. Consider the following
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
The following attributes defines the equilibrium of supply, demand and trade in a single industry
The Import demand = export supply, this translates to the following
Home demand- Home supply = Foreign supply- Foreign demand
This analysis brings us to the benefits attributed to the costs and tariffs in the world equilibrium
Costs and Tariffs
In the international trade where imports and exports occur, a tariff plays a critical role in the world trade equilibrium. This is a cost that can be likened to the transportation cost whose influence makes the sellers shy away from shipping products unless the Home price is more than the foreign price (Gandolfo, 1995). In most cases, the exceeding amount must be equal to the tariff amount so as to have a profit. The increase of price in the local market and the decrease of price in the foreign market are immensely attributed to a tariff. Consider the following illustration of effects of tariff on various types of markets
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
In the case of the world market, as the price increases, a drop in the quantity is recorded.
Effects of tariff in a small country
Small nations have insignificant demand for goods relative to the world demand and this makes them less influential on the foreign price (Gandolfo, 1995). This explains the reason why the foreign price does not change when small nations are considered. However, the home price increases by the whole amount of the tariff and this is primary disadvantage small nation face when participating in the international trade (Gandolfo, 1995). This effect of tariffs on small nations explains the reluctance of numerous small nations participating actively in the international trade. Consider the following illustration on the effect of a tariff on a small nation
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
In cases of policy changes the effective rate of protection is factored in depending on the change in value in a particular industry, which is added into the production process. This depends entirely on the variation in prices and trade policy (Gandolfo, 1995). It is imperative to note that, the effective rates of protection fluctuate from tariff charges since the tariffs influence various sectors besides the protected one. Consider the following example
The mobile sells in the global market for $ 10000, from $ 8000 factors of production, the value that is added to the overall production cost will be calculated as follows
$10000-8000 = 2000
In the event a nation imposes a 20% tariff on the imported mobiles the home firms can charge $12,000 instead of $10,000.
This translates to the effective protection for home mobile firms of 100% as computed as follows
4000-2000/2000 = 100%
Effective rate of protection > tariff rate
Some of the costs and benefits attributed to tariffs include the increase of the cost of an imported product which is disadvantageous to the consumers while it increases the profitability of the producers. Further the various governments involved in the international trade gains the tariff revenues. Consider the following illustration which indicates the costs and benefits to consumers, producers and the governments.
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
Export subsidy
This can either be specific whereby it implies payment for each unit exported is made or ad valorem whereby a portion of the total value of the exported is paid. Some of the effects attributed to the export subsidy include damage to the national welfare in terms of efficiency as indicated in the graph. This aspect of efficiency arises in a situation where by the producers are attempted to produce so much that the consumers could not fully consume due to their limited desire. Consider the following graph indicating the effects created to consumers, producers and government by tariffs.
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
Import Quota
This refers to a restraint on the amount of a particular product that may be imported. This is imposed by the issuance of licenses and rights relative to the quota system. Application of the quota system is disadvantageous to the government because the intended revenues attributed to the selling of imports at lofty prices are directed to the license holders (Gandolfo, 1995). The excess revenues are referred to as the quota rents. Similarly the voluntary export quota requested by the exporting nations works the same as the import quota. The following illustration is a good example on how the import quota influences sugar.
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
Balance of Payments
This is a critical part of the monetary economics relative to the international trade. They are divided into classes which include current and capital accounts. In the case of current accounts, it deals with the flow of goods and services. On the other hand, the capital account deals with the flow of finical assets and in some cases other various kinds of assets (Gandolfo, 1995). The aspect of the double entry characterizes the each transaction of the balance of payments and the following equation
Current account +capital account =0
Gross National Product (GNP)
This refers to the value of the total final goods and services that a nation’s factors of production are able to produce in a particular period. Factors of production imply the attributes of labor, capital and natural resources. For instance, the US-owned factors of production are termed as the US-GNP (Gandolfo, 1995). Consider the following illustration of the US-GNP and its attributed components
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
Money Control
Money is a medium of exchange and it requires particular control to ensure that the business market is ideal for transactions. In most cases, the central bank takes charge of controlling the amount of money which circulates in an economy. This aspect is called money supply. On a similar note, the aspect of money demand refers to the quantity of money in terms of assets which people are willing to hold at a particular time (Gandolfo, 1995). The demand for money is influenced by interest rates, risks and liquidity. The aggregate real money demand and the interest rate is illustrated in the graph below
Source: Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
References
Gandolfo, G. (1995). International economics: 2. Berlin [u.a.: Springer.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF International Monetary Economics
Balance of Payments Accounts
(Kenen, 2000) The interrelationship between the balance of payments and the exchange rate regimes is one of the key relationships in economics.... This paper ''Balance of Payments Accounts'' tells us that Balance of Payments accounts for the overall level of transactions a country conducts with the rest of the world during a year....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Essay
Economic and Monetary Union in Europe
Moreover, there are a number of alternative sets of monetary arrangements that are in theory consistent with monetary union such as currency union, exchange rate union, free inter-circulation union, parallel currency union etc.... The concept of an international monitory system has evolved during the initial half of twentieth century as a result of the 1930 financial crisis and the problems faced by the countries.... In the 1940's America and Britain tried to introduce an international monitory system under the label of Bretton Woods....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Assignment
Financial Issues in BP Pipeline
Opportunity cost is one of the most used concepts in economics.... It covers information on opportunity cost, national debt, budget deficit, the money supply in the economy, and monetary options and tools.... Macroeconomic policies involve fiscal policy concerned with government expenditure, revenue collection, and monetary policy....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Essay
Global Balance of Payments of the European Union
This essay "Global Balance of Payments of the European Union" discusses European provinces are controlled together in terms of certain policies that are framed and structured by the European monetary Union.... The monetary inflexibility of the policies in the EMU is becoming difficult when followed under the current economic operations of different nations.... The rigid policies of EMU prevent the monetary authorities in different countries to undergo the process of deficit financing that would help the nations to pay out their creditors....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Essay
International Finance - financial stability
Often called also International Monetary Economics or international macroeconomics, each term has a slightly different meaning, and none seems entirely right for the entire field.... According to the Deardoff's Glossary of International economics, "International finance is the monetary side of international economics, in contrast to the real side, or real trade.... o explain international economics, it is the interaction among countries with respect to financial transactions, trade relationships, organizations and policies that govern them....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Essay
Consider how a currency appreciation might affect national income
Factors such as relative product prices, monetary policy, inflation rate differences and income changes influence the appreciation of a country's currency (LIPSEY & CHRYSTAL, 2011 p 167).... ountries that implement restrictive monetary policies will be decreasing the supply of their currency hence currency appreciation....
5 Pages
(1250 words)
Essay
International Monetary Economics, Bretton Woods Agreement
The paper "International Monetary Economics, Bretton Woods Agreement " is an outstanding example of a macro & microeconomics assignment.... The paper "International Monetary Economics, Bretton Woods Agreement " is an outstanding example of a macro & microeconomics assignment.... Given the stances and destruction of World War II, the world's leading nations gathered at Bretton Woods in 1944 for establishing a new international monetary system to avoid previous mistakes (Bordo, Michael and Barry)....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Assignment
Following Economies Currency and the Interest Rates
The most influencing factor was Russia's annexation of Crimea in Ukraine.... As reported by the Matlack (2014), by October last year, the rubble was down by 20% in comparison to the US dollar.... It has been described as.... ... ... The paper "Following Economies' Currency and the Interest Rates" is a great example of a macro & microeconomics assignment....
9 Pages
(2250 words)
Assignment
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the on your topic
"International Monetary Economics"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY