StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Macro & Microeconomics
- Implications for the Financial Sector and Chinese Economic Growth
Free
Implications for the Financial Sector and Chinese Economic Growth - Example
Summary
I’m still writing your paper. But I assure you that the completed paper will be uploaded asap. Please forgive me for the delay. I have been suffering from migraines and dizziness these past few days. Kindly ignore the completed…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER96.6% of users find it useful
- Subject: Macro & Microeconomics
- Type:
- Level: Ph.D.
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: volkmangabe
Extract of sample "Implications for the Financial Sector and Chinese Economic Growth"
dear client, this is not yet the final paper. I’m still writing your paper. But I assure you that the completed paper will be uploaded asap. Please forgive me for the delay. I have been suffering from migraines and dizziness these past few days. Kindly ignore the completed status of your paper. Thank you!
Due to China’s historical development and size, its reform dynamics so far has been one of a kind. Massive changes in the Chinese economy began much earlier than the transformation of comparable economic structures of the Baltic States and Eastern Europe. China’s financial reforms have been slow, and its beginnings were quite unique from that of other large economies that tried to change their systems. To a certain extent, China’s financial reforms were more similar to the transformation of several East Asian economies than those of numerous previously centrally planned economies.
From January 2009-2010, the foreign portfolio investment in the Shanghai Stock Exchange Composite Index (SSECI) is turning around. This implies that as the global financial crisis intensifies, developed nations’ financial institutions are trading their shares of China’s state-owned investment banks (Spence & Leipziger 2010). As indicated in the statements of the People’s Bank of China, the foreign reserves of the country have swelled in 2008, in spite of the obvious foreign investment outflow (Min-Chan 2009). Nevertheless, the boost in foreign reserves was brought about by the exchange rate fluctuations. In fact, an outflow of approximately US$25 billion was experienced by China in December only, and at some point in the fourth quarter of 2008 a sum of US$150 billion was pulled out from the country, according to the report of the Bank of China (Min-Chan 2009, 43).
The dramatic economic growth of China has to a certain extent been fuelled by its thriving export-driven production. Nevertheless, the export of China by mid-2008 diminished to a ‘negative 20-percent growth rate from the positive 20-30 percent rate in previous years’ (Platt 2009, 50). Because of these developments some financial analysts predicted that China would confront a financial crisis in 2009 and 2010. The prediction happened and this forced the Chinese government to initiate a set of stimulus package (Yao & Zhang 2011). These attempts of China to recover from the global financial crisis will be analyzed in this paper.
The Recovery Attempts of China’s Stock Market
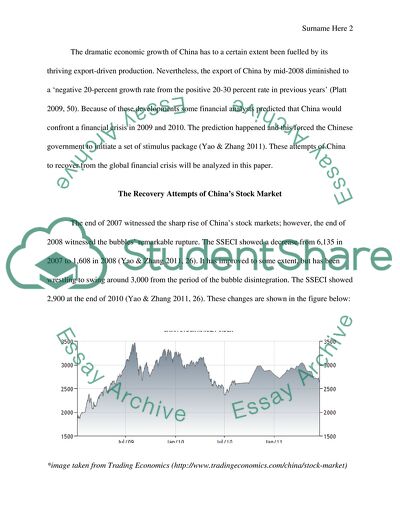
The end of 2007 witnessed the sharp rise of China’s stock markets; however, the end of 2008 witnessed the bubbles’ remarkable rupture. The SSECI showed a decrease from 6,135 in 2007 to 1,608 in 2008 (Yao & Zhang 2011, 26). It has improved to some extent, but has been wrestling to swing around 3,000 from the period of the bubble disintegration. The SSECI showed 2,900 at the end of 2010 (Yao & Zhang 2011, 26). These changes are shown in the figure below:
*image taken from Trading Economics (http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/stock-market)
China exposed the avenues to new share offerings, letting loose a stream of initial public offerings (IPOs) to aid in the absorption of surplus liquidity and calm a raging stock market. What began as a drop of IPOs became a surge, with numerous companies primed to register in the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Platt 2009).
According to Michael Guillen, professor of international management and director of the Lauder Institute, in his remark about the recovery attempts of China’s stock market in the Financial Times (2009), “During the last two years, monetary policy has been unusually loose. It aimed at rescuing the financial sector from oblivion and ensuring that there is enough liquidity in the system to revive credit. Inflation is low or negative in China” (ibid, para 46). Likewise, The Economist (2008) claims that the Chinese government has to control too much liquidity in order to lessen the possibility that China is beginning to pump up its largest bubble ever recorded.
Borrowing the analysis of Yao and Zhang (2011), the Chinese government should also look at the causes of the sudden drop of SSECI at the end of 2008, and target these causes in its recovery efforts. Primarily, majority of shareholders allocate their resources in the housing market thus pumping up the housing bubble. In addition, there was a large-scale dilution impact brought about by initial public offerings and new shares by listed companies. And lastly, listed companies did not give dividends, showing the uncertainty of private shareholders and the listed companies’ disregard of corporate social responsibility.
Prospects of Financial Regulatory Reforms and their Implications for the Financial Sector and Chinese Economic Growth
The government of China prepares to tries to encourage consumer spending as a strategy to shake off diminishing exports and the resulting financial crisis. It is expressing determined goals to sustain an economic expansion of 8% by putting into effect the wide-ranging stimulus package (Min-Chan 2009). China’s fiscal and monetary policies involve improving potential investments to cope with the current financial crisis, but this policy will be unsound since the government can merely furnish the needed resources for only a given period of time. The centre of the recovery of China’s stock markets should be increase in exports instead of an imposing stimulus package (Haddad & Shepherd 2011). While the worldwide financial crisis endures, the government of China will arrive at economic development by boosting fiscal spending.
Fiscal Policy
China launched a huge fiscal stimulus package in November 2008. This proclaimed package shows the persistent belief of the Chinese government in advancing economic growth thru huge amounts of investment (Spence & Leipziger 2010). The objectives of this fiscal stimulus plan involve health and education, technological development, cheap housing, environmental venture, rural infrastructure, power infrastructure, and transportation (Spence & Leipziger 2010).
Monetary Policy
The $586 billion monetary stimulus plan of the Chinese government intends to protect China from a worldwide recession by bringing in cash into the economy through investing on public infrastructures (Qiren 2010, 8). However, its primary objective is to enhance consumer spending (ibid, p. 8).
The two completely distinct economic results in China and the United States, after a period of the most serious economic and financial crisis in eight decades, obviously have large-scale repercussions for economic theory and practice (Haddad & Shepherd 2011). The different outcomes of the fiscal and monetary policies of China and the U.S. are rooted in economic system and ideology (Spence & Leipziger 2010). The dominant ideology in the United States is that government interference is unfavourable hence a major plan of government spending should not be carried out even if private investment was dropping hastily (Haddad & Shepherd 2011). Nonetheless, even when this ideology had been abolished, the U.S. has no structures able to carry out a major plan of increased government spending (Haddad & Shepherd 2011). The established government investment in the United States is merely 3.5 percent of GDP (Spence & Leipziger 2010, 84), a negligible source from which to overturn the effects of the magnitude of losses in private investment which took place.
Discussions and Conclusions
So where is the recovery of China’s stock markets heading to? Uncertainties are ever-present that China’s financial and monetary recovery is not stable and remains shaky. Under the aforementioned requirements, the tempo of China’s economic development will speed up on the condition that its exports start to recuperate sooner than later. The predicted growth in the United States will also improve the exports of China.
An issue that every country should take into consideration is the potential cost of their stimulus plans to save the weakening global economy. This also applies to China, a nation that has initiated stimulus programmes to monitor and curb its economic crisis. The stream of monies in different sectors is predicted to elevate the prices of local products/services eventually. This fact makes it crucial for China to give significance to the inflation issue and put into effect efficient strategies/policies to reduce the threats of inflations.
References
Financial Times. “China’s Role in the Global Recovery,” (1 September 2009): http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/2df3ea66-9716-11de-83c5-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1Q8q9b0Pz
Haddad, M. & B. Shepherd. Managing Openness: Trade and Outward-Oriented Growth After the Crisis. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications, 2011.
Min-Chan, P. “China: Aiming for 8% Growth Despite the Financial Crisis,” SERI Quarterly 2.2 (2009): 43+
Platt, G. “China Removes IPO Ban as Market Soars,” Global Finance 23.8 (2009): 50.
Qiren, Z. “Some Reflections on the Post Crisis Period,” China Daily (2010): p. 8
Spence, M. & D. Leipziger. Globalisation and Growth: Implications for a Post-crisis World. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications, 2010.
The Economist. “Bull in a China Shop,” (8 October 2009): http://www.economist.com/node/14587130
Yao, S. & J. Zhang. “Chinese Economy 2010: Post Crisis Development,” China Policy Institute Issue 67 (2011): pp. 2-30.
Read
More
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Implications for the Financial Sector and Chinese Economic Growth
Macroeconomic Convergence, Financial Development and Economic Growth: China
The paper "Macroeconomic Convergence, Financial Development and economic growth: China" highlights that economic growth in China provides opportunities and challenges in the global economy.... Since then the nation has experienced steady and rapid growth of per capita economic growth which is among the highest rates in global economic history.... This dramatic post-1978 economic growth has been attributed to numerous global and internal factors....
13 Pages
(3250 words)
Literature review
Macro & Micro economics
The government has vowed to guide the financial institutions, to make them operate prudently, oversee the financial activities of the institutions and take account of the risks associated with off-balance sheet activities, so as to make the financial sector's more sustainable and capable of supporting long term economic development.... This would ensure steady economic growth.... While bringing economic growth the government aims at keeping the price level in the economy stable and guard against the occurrence of any regional or systemic financial risk....
6 Pages
(1500 words)
Essay
Recovery of the China Stock Market and Challenges in the Post-Crisis Era
he dramatic economic growth of China has to a certain extent been fuelled by its thriving export-driven production.... ccording to Michael Guillen, professor of international management and director of the Lauder Institute, in his remark about the recovery attempts of China's stock market in the financial Times (2009), “During the last two years, monetary policy has... Nevertheless, the export of China by mid-2008 diminished to a ‘negative 20-percent growth rate from the positive 20-30 percent rate in previous years' (Platt 2009, 50)....
4 Pages
(1000 words)
Essay
Critical Analysis of Chinas Economy
This essay focuses on comprehending the efforts applied in ensuring economic growth.... Over the past years, China has portrayed relentless economic growth as compared to other countries in East Asia.... However, in the contemporary world, the population comprises of the unemployed youth contrary to the economic growth.... It is believed that China made its breakthrough in economic growth during the Song Dynasty.... As a result, China acquired the global superpower rank in economic growth....
7 Pages
(1750 words)
Research Paper
The Role of De-Regulation of the Financial System
"The Role of De-Regulation of the financial System" paper highlights deregulation and its role towards the financial system to advance the interests of finance capital.... In various instances, the deregulation acts have been imposed focusing on the financial systems of industrial sectors in various countries.... For example, one of the most crucial changes in the financial system's regulations was the Gramm-Leach- Bliley Act, which was enacted in the US in the year 1999....
3 Pages
(750 words)
Essay
Chinas Strategy during Global Financial Crisis
In the United States and Europe, the crisis emerged in the financial sector and it subsequently spread to the real economy.... According to Saez (2004), as part of financial sector reforms, China had taken aggressive measures to recapitalize major banks, restructure its corporate governance systems, and make banking regulations more stringent.... Referring to the words of Crotty (2009), they identified inadequate financial regulation, loosening of banking policies, extreme financial innovation, and Wall Street greed as the root causes of the financial breakdown....
11 Pages
(2750 words)
Essay
Causes and Implications of the Global Financial Crisis
This implies that many borrowers could not be able to repay the mortgages and this affected the performance of other markets globally leading to the financial crisis.... The first cause is the growth of the housing bubble in America.... The paper 'Causes and Implications of the Global financial Crisis' is an impressive example of the macro & microeconomics essay.... The global financial crisis is the situation where many consumers and businesses face difficulties in terms of the economy....
9 Pages
(2250 words)
Essay
Current Financial Market Events and Their Implications
To begin with, the global economic crisis led many countries to have outstanding debts.... The paper "Current financial Market Events and Their Implications" is an inspiring example of a research paper on finance and accounting.... The paper "Current financial Market Events and Their Implications" is an inspiring example of a research paper on finance and accounting.... The paper "Current financial Market Events and Their Implications" is an inspiring example of a research paper on finance and accounting....
12 Pages
(3000 words)
Research Paper
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the on your topic
"Implications for the Financial Sector and Chinese Economic Growth"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY