StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Finance & Accounting
- Cost Accounting: Product and Absorption Costing
Free
Cost Accounting: Product and Absorption Costing - Book Report/Review Example
Summary
The paper “Cost Accounting: Product and Absorption Costing” seeks to examine absorption costing, which is cost accounting technique which expenses the associated costs of manufacturing a given product. This method uses the total direct material cost, direct labor cost, and direct overhead cost…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER96.5% of users find it useful
- Subject: Finance & Accounting
- Type: Book Report/Review
- Level: Business School
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 0
Extract of sample "Cost Accounting: Product and Absorption Costing"
Cost Accounting: Product and Absorption Costing
Absorption costing
Absorption costing is cost accounting technique which expenses the associated costs of manufacturing a given product (KHAN, & JAIN, 2000). This method uses the total direct material cost, direct labor cost and direct overhead cost which relates to production of a particular product as the cost base. In other wards all the manufacturing costs are engrossed by the units’ produced. The cost of output inventory will include direct raw materials consumed, direct labor, related variable costs and fixed production overheads (CHADWICK, 1999). As the name suggests it can also be called full costing. This managerial cost accounting method is very essential because it is a requirement by Generally Accepted Accounting Principle-GAAP for f income tax reporting and external financial reporting.
Absorption costing is frequently compared with direct costing or variable costing. Whenever the direct or variable costing is adopted by a given organization, the fixed production overhead costs are not assigned or apportioned to the products manufactured. This kind of costing is over and over again useful for decision-making in managerial cost control. The absorption costing principle is mostly applicable when preparing compressive income statements. One of the input principles of absorption costing is that units of inventory produced should include both variable and fixed cost incurred in making them to their final state of production. This method presupposes that purchasers and consumers do not respond to prices at all when making their choices to purchase the product (RAJASEKARAN, & LALITHA, 2011).
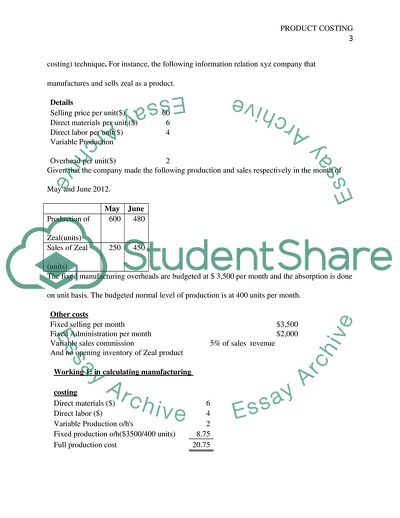
It also assumes that clientele will purchase the projected unit sales irrespective of their price that is tagged on them. It is imperative to keep in mind this when using this method (absorption costing) technique. For instance, the following information relation xyz company that manufactures and sells zeal as a product.
Details
Selling price per unit($)
60
Direct materials per unit ($)
6
Direct labor per unit($)
4
Variable Production Overhead per unit($)
2
Given that the company made the following production and sales respectively in the month of May and June 2012.
May
June
Production of Zeal(units)
600
480
Sales of Zeal (units)
250
450
The fixed manufacturing overheads are budgeted at $ 3,500 per month and the absorption is done on unit basis. The budgeted normal level of production is at 400 units per month.
Other costs
Fixed selling per month
$3,500
Fixed Administration per month
$2,000
Variable sales commission
5% of sales revenue
And no opening inventory of Zeal product
Working 1: in calculating manufacturing costing
Direct materials ($)
6
Direct labor ($)
4
Variable Production o/h's
2
Fixed production o/h($3500/400 units)
8.75
Full production cost
20.75
Working 2: calculation of the value of inventory and production (these must be valued in $ 20.75 per unit produced)
Opening inventory
Production
Closing inventory
May
0
600x20.75=$12,450
350x20.75=$7,262.5
June
350x20.75=$7,262.5
480x210.75=$9,960
380x20.75=$7,885
Working 3: Over/under absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead
May
June
Actual fixed production overhead
$3,500
$3,500
Fixed overhead absorbed
600x8.75=$5250
($1750 over absorbed)
480x8.75=$4200
($ 700 over absorbed)
Therefore comprehensive income statement of Absorption costing would be as follows:
May($)
May($)
June($)
June($)
Sales
15,000
27,000
Opening inventory(W2)
0
7262.5
Production (W2)
12,450
9,660
Closing inventory (w2)
(7,262.5)
(5,187.5)
(7885)
(9,037.5)
Over absorption of fixed manufacturing overhead
1750
700
Gross profit
8062.5
18,662.5
Less expenses
Variable sales commission
(750)
(1,350)
Fixed administration cost
(2,000)
(2,000)
Fixed selling
(3,500)
(3,500)
Net profit
18,125.5
11,812.5
Strengths of Absorption Costing:
Absorption costing recognizes the importance of fixed costs in producing goods and services. Fixed cost refers to those costs which do not change irrespective of the output level or sales revenue, such as insurance, rent, salaries, insurance and wages. Costs do vary over time hence we cannot classify cost as purely fixed cost. Fixed costs concept is important in the short term cost accounting.
Absorption costing is accepted by Inland Revenue as stock is not rated too low; this is significant in this type of costing since the revenue can be easily recognized from unsold stock. It is constantly used to prepare financial accounts hence provides a true and fair financial records to various users of the accounts. Since absorption costing takes care of variable and total cost, it is easier for management to know how to reduce cost.
Absorption costing will show less fluctuation in net profit when production remains constant but sales fluctuate, on the contrary, marginal costing where fixed costs do change into variable cost, it is cost into the stock value therefore disfiguring valuation of stock (BHATTACHARYYA, 2011).
Weaknesses of Absorption Costing:
Absorption costing does not provide useful information to management to make decisions and control planning since it lays its emphasis on total cost such as variable and fixed cost.
Cost volume profit relationship is ignored because the emphasis is laid on the total cost by management.
Absorption costing is a technique of inventory costing wherein every fixed manufacturing costs and variable manufacturing costs are taken in as inventorial costs (JACKSON, ET AL 2009).
In the product and service costing, an absorption costing system allots a share of every cost earned by a production to each of its products and services. This way, it can be recognized whether, in due course, each product and service makes revenue.
In product or service costing, absorption costing system lays more emphasis on the behavioral, and not the functional, cost characteristics. We have to separate costs into variable and fixed elements (taking into consideration that the total cost remains the same in each period despite activity level). This cannot be achieved accurately with ease, and is an overview of reality, the information regarding costing can be very helpful for planning, decision making and control that are short term, particularly in a multi-product business.
In this costing system, sales minus variable costs determines the input that products/services of individuals make in relation to the total fixed costs gained by the business. The fixed costs are treated as period costs and, per se are simply deducted from contribution in the period incurred to get net profit. Certain assumptions have to be made while absorption costing is derived. Such assumptions states that consumers are not affected by the price changes and that they will continue buying goods and services irrespective of change in price. According to the law of demand more consumers buy goods and services when their prices fall. Few consumers will be seen buying the same goods and services when prices rises (WEYGANDT, ET AL 2010). When a business enterprise is dealing with absorption costing, this assumption has to be made in order to take care of fixed and total cost. Change in price of a commodity does affect the demand of that commodity. This assumption is criticized because there is no way that an increase in price of a commodity will still attract more consumers to it. A reduction in price will enable more consumers to purchase since they will have purchasing power (LAL, & SRIVASTAVA, 2009).
The recommendations
Welsh Government is a public sector organization which is required to accou8ntable to public in general for that reason, should be reporting to the external parties. This makes the absorption costing appropriate method for external reporting (DRURY, 2007). The presumptions, that purchasers and consumers do not respond to prices at all when making their choices to purchase the product makes it commendable for Government budgeting which is base on estimates. It also keeps budgetary interlink (expenditure) accounts and cost account in future focusing in a constant growing economy (DU TOIT, 2007). Governmental body being a non profit making would not be required to produce an operating statement which in fact are reflected in comprehensive income statement of Absorption costing absorption. Consequently, it will fit an accrual basis of accounting which is hugely used by public sector accounting methods. Being of great beneficial to cost control procedure in that it makes no distinction between variable and fixed costs reflects the objectivity of the method of costing.
References
BHATTACHARYYA, D. (2011). Management accounting. Delhi, Pearson.
CHADWICK, L. (1999). Management accounting. London, Internat. Thomson Business Press.
DRURY, C. (2007). Management and cost accounting. London, Thomson Learning.
DU TOIT, E. (2007). Cost and management accounting. Cape Town, Pearson Maskew Miller Longman.
JACKSON, S., SAWYERS, R., & JENKINS, G. J. (2009). Managerial accounting: a focus on ethical decision making. Mason, OH, South-Western.
KHAN, M. Y., & JAIN, P. K. (2000). Cost accounting. New Delhi, Tata McGraw-Hill Pub. Co. Ltd.
LAL, J., & SRIVASTAVA, S. (2009). Cost accounting. New Delhi, Tata McGraw-Hill.
RAJASEKARAN, V., & LALITHA, R. (2011). Cost accounting. Delhi, Pearson.
WEYGANDT, J. J., KIESO, D. E., & KIMMEL, P. D. (2010). Managerial accounting: tools for business decision making. Hoboken, NJ, Wiley.
Read
More
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the book report/review on your topic
"Cost Accounting: Product and Absorption Costing"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY