StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Finance & Accounting
- Bonds and Derivatives as Main Financial Instruments
Free
Bonds and Derivatives as Main Financial Instruments - Assignment Example
Summary
The paper “Bonds and Derivatives as Main Financial Instruments ” is a comprehensive example of a finance & accounting assignment. This article focuses mainly on understanding the two main financial instruments which are bonds and derivatives…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER94.1% of users find it useful
- Subject: Finance & Accounting
- Type: Assignment
- Level: Business School
- Pages: 5 (1250 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: jakayla69
Extract of sample "Bonds and Derivatives as Main Financial Instruments"
This article focuses mainly at understanding the two main financial instruments which are bonds and derivatives. The company that is selected for theanalysis of bonds and derivatives is HP, one of the giant in manufacturing computing units. The first section is based upon the bonds and then followed by derivatives.
Bonds (Notes)
The long-term debts of HP constitute broadly three different kinds on notes. These are:
US Dollar Global Notes
EDS Senior Notes
Other Notes including capital lease Obligations
In the following paragraphs, the sub-kinds of the above mentioned notes are discussed.
1) US Dollar Global Notes
These notes are primarily issued by HP thrice in last decade including 2002 shelf registration, 2006 shelf registration and 2009 shelf registration. 2002 shelf registration consists of “$500 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.505% in June 2002 at 6.5%, due July 2012”. The other different types of bonds issued by HP, their face value, total amount, type of bonds (fixed, floating), maturity, interest rates and the issue prices are detailed below.
These details are reproduced from the annual report of HP for the year 2010.
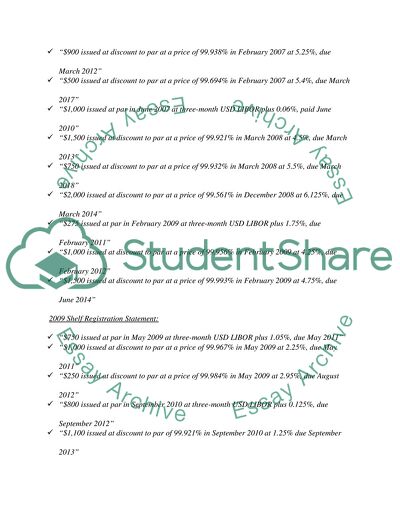
2006 Shelf Registration Statement:
“$600 issued at par in February 2007 at three-month USD LIBOR plus 0.11%, due March 2012”
“$900 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.938% in February 2007 at 5.25%, due March 2012”
“$500 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.694% in February 2007 at 5.4%, due March 2017”
“$1,000 issued at par in June 2007 at three-month USD LIBOR plus 0.06%, paid June 2010”
“$1,500 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.921% in March 2008 at 4.5%, due March 2013”
“$750 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.932% in March 2008 at 5.5%, due March 2018”
“$2,000 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.561% in December 2008 at 6.125%, due March 2014”
“$275 issued at par in February 2009 at three-month USD LIBOR plus 1.75%, due February 2011”
“$1,000 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.956% in February 2009 at 4.25%, due February 2012”
“$1,500 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.993% in February 2009 at 4.75%, due June 2014”
2009 Shelf Registration Statement:
“$750 issued at par in May 2009 at three-month USD LIBOR plus 1.05%, due May 2011”
“$1,000 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.967% in May 2009 at 2.25%, due May 2011”
“$250 issued at discount to par at a price of 99.984% in May 2009 at 2.95%, due August 2012”
“$800 issued at par in September 2010 at three-month USD LIBOR plus 0.125%, due September 2012”
“$1,100 issued at discount to par of 99.921% in September 2010 at 1.25% due September 2013”
“$1,100 issued at discount to par of 99.887% in September 2010 at 2.125% due September 2015”
2) EDS Senior Notes:
“$1,100 issued June 2003 at 6.0%, due August 2013”
“$300 issued October 1999 at 7.45%, due October 2029”
3) “Other, including capital lease obligations, at 0.59%-8.63%, due in calendar year 2010-2024”
The total book value of these debts is around $15,258 million after the subtracting the current portion of these debts which is part of current liabilities. The promising feature of the HP bonds or notes is that they are callable in part or in full whenever HP deems it necessary at the prices and criterion specified under its prospectus. These Global Notes are considered to be the senior unsecured debt.
As at October 31, 2010 the face value of the long-term debts that are maturing in upcoming years have been segregated year wise in table given below. These long-term debts are free from any fair value adjustment, premium or discount on issuance.
“Aggregate future maturities of debt outstanding including capital lease obligations”
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
Thereafter
Total In millions
$2,208
$4,272
$3,775
$3,720
$1,111
$1,691
$16,777
Source: HP Annual Report 2010
Derivatives
Being a global company, HP normally faces interest rate changes and foreign currency exchange rate movement as a result HP hedges these fluctuations by utilizing derivative contracts. HP generally uses forwards, options, swaps and total return swaps as part of its risk management strategy to combat with risks related to interest rate exposure, foreign currency exchange rate exposure and equity exposures. Therefore, in order to protect the fair values of assets and liabilities, gains and losses which arise as a result of these exposures are mainly offset by the respective gains and losses of the related derivative contracts so that the volatility of earnings can be minimized. Derivatives used by HP as a hedging activity and does not have any relation with speculations. Normally HP categorizes the derivates as fair value, cash flow and other hedges as the main types of hedging. Other hedges mainly include economic hedges. In the consolidated balance sheet, these derivative instruments are carried at their fair values in the heads of “other current assets” and “long-term financing receivables” in the asset side. For liabilities, these derivatives are placed in accrued and other liabilities. In consolidated cash flow statement, these derivatives are classified into operating activities.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk or default risk is always an inherent risk when dealing with derivatives. The risk that exposes HP to counterparty risk is the inability of counterparty to meet with the contractual obligations. In order to minimize the counterparty risk, HP has formulated a framework or guideline when entering into derivative contracts with other parties. These guidelines consider the financial health, credit rating, creditworthiness and other factors related to counterparties. One the better policies that HP has developed to reduce the likelihood of the counterparty risk, is the usage of netting arrangements. These netting arrangements only make both the parties liable to pay each other only in case of having gains or losses.
Fair Value Hedges
Fair value hedges used by HP are mainly aimed at hedging the interest rate risks in relation to debt portfolio maintained by HP. Since HP has issued wide level of US dollar bonds, therefore, HP is exposed to interest rate risk. For floating bonds, HP uses interest rate swaps, to combat with the market interest rate risk. Generally, these swap transactions include fixed for floating payments or floating for fixed payments. These swap arrangements are made when market conditions are favorable to HP. Another variant indicated by HP is the interchangeability of variable and fixed streams of interest payments. These swap related derivatives are recognized as fair value hedges in which the gains or losses arising as a result of these swap arrangements are directly recognized in the current period in income statement.
Cash Flow Hedges
For net revenues, cost of sales, other operating expenses, leasing arrangements related in intercompany that that are denominated in currencies other than US dollars, cash flow hedges are used by HP and forwards and options are mainly used as a primary derivative contract by HP to reduce the risks related to exchange rate exposures. Normally a period of six to twelve months is used by HP for cash flow hedges. But, on the other hand, due to extended duration of lease terms, a period of five years for forward contracts, are also used. The criterion used to recognize the cash flow hedges in the financial statements, HP recognizes the gains and losses arising from cash flow hedges in the comprehensive income. In the past three years, no cash flow hedge is discontinued by HP on the qualification grounds.
Other Derivatives
In order to protect against foreign currency balance sheet risks, forward contracts are mainly used as a hedging tool by HP. For hedging against the fluctuations of executive deferred compensation plan, HP utilizes total return swaps and interest rate swaps on the basis of both fixed income and equity indices. There are some derivatives which are not used as a hedging tool by HP those derivatives are recognized into income statement in the period in which they reflect a change at their fair values.
Hedge Effectiveness
Effectiveness of hedging in case of interest rate swap is computed “by offsetting the change in fair value of the hedged debt with the change in fair value of the derivative”. In order to measure the effectiveness for options and swaps which are categorized as cash flow hedges, “cumulative change in the hedge contract with the cumulative change in the hedged item, based on the forward rate”
References
Hewlett Packard. (2010). Hewlett Packard Company Annual Report. Washington DC: Apotheker, Leo.
Read
More
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the assignment on your topic
"Bonds and Derivatives as Main Financial Instruments"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY